Bigelow Expandable Activity Module
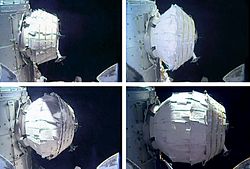
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is an experimental expandable space station module developed by Bigelow Aerospace, under contract to NASA, for testing as a temporary module on the International Space Station (ISS) from 2016 to at most 2028, when the contract can not be further extended. It arrived at the ISS on 10 April 2016, was berthed to the station on 16 April 2016, and was expanded and pressurized on 28 May 2016. Although originally planned to be a two year test, it has exceeded expectations and is used as additional cargo storage. The module is under ownership of NASA after Bigelow Aerospace suspended operations in 2021.
 Full-scale mock up of BEAM at Johnson Space Center | |
| Mission type | Inflatable ISS Module |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 2016-024A |
| Mission duration | == Bigelow Expandable Activity Module Media ==
(in progress) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 8 April 2016, 20:43:31 UTC |
| Rocket | Falcon 9 Full Thrust (SpaceX CRS-8) |
History
NASA originally considered the idea of inflatable habitats in the 1960s, and developed the TransHab inflatable module concept in the late 1990s. The TransHab project was canceled by Congress in 2000, and Bigelow Aerospace purchased the rights to the patents developed by NASA to pursue private space station designs. In 2006 and 2007, Bigelow launched two demonstration modules to Earth orbit, Genesis I and Genesis II.
NASA re-initiated analysis of expandable module technology for a variety of potential missions beginning in early 2010. Various options were considered, including procurement from commercial provider Bigelow Aerospace, for providing what in 2010 was proposed to be a torus-shaped storage module for the International Space Station. One application of the toroidal BEAM design was as a centrifuge demo preceding further developments of the NASA Nautilus-X multi-mission exploration concept vehicle. In January 2011, Bigelow projected that the BEAM module could be built and made flight-ready 24 months after a build contract was secured.
On 20 December 2012, NASA awarded Bigelow Aerospace a US$17.8 million contract to construct the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) under NASA's Advanced Exploration Systems (AES) Program. Sierra Nevada Corporation built the US$2 million Common Berthing Mechanism under a 16-month firm-fixed-price contract awarded in May 2013. NASA plans made public in mid-2013 called for a 2015 delivery of the module to the ISS.
In 2013, it was planned that at the end of BEAM's mission, it would be removed from the ISS and burn up during reentry.
During a press event on 12 March 2015, at the Bigelow Aerospace facility in North Las Vegas, Nevada, the completed ISS flight unit, compacted and with two Canadarm2 grapple fixtures attached, was displayed for the media.
In December 2021, Bigelow transferred ownership of BEAM to NASA's Johnson Space Center. With the cessacion of Bigelow Aerospace activities, NASA contracted ATA Engineering, a former Bigelow subcontractor, for engineering support on the BEAM.