Condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics which talks about matter that has its molecules packed together very closely. This usually means it deals with solids (solid matter).
Condensed Matter Physics Media
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes and Johannes van der Waals with the helium liquefactor at Leiden in 1908
A replica of the first point-contact transistor in Bell labs
A magnet levitating above a high-temperature superconductor. Today some physicists are working to understand high-temperature superconductivity using the AdS/CFT correspondence.
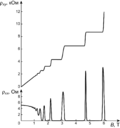
The quantum Hall effect: Components of the Hall resistivity as a function of the external magnetic field: Script error: The function "hyphen2dash" does not exist. 
Image of X-ray diffraction pattern from a protein crystal
The first Bose–Einstein condensate observed in a gas of ultracold rubidium atoms. The blue and white areas represent higher density.
Computer simulation of nanogears made of fullerene molecules. It is hoped that advances in nanoscience will lead to machines working on the molecular scale.