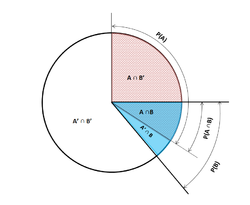
Conditional probability
In probability theory, conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring, given that another event has occurred. Usually this is written as [math]\displaystyle{ P(A\mid B) }[/math]. This is read as "probability of A given B". The two events need not be related. They also need not occur at the same time. In the most general case,
[math]\displaystyle{ P(A\mid B) = \frac{P(A\cap B)}{P(B)} }[/math]
Expressed in words: The conditional probability of A occurring given B is the probability of both events occurring, divided by the probability of B occurring. As a division by zero is not defined, the probability of B occurring must not be zero.
Conditional Probability Media
Illustration of conditional probabilities with an Euler diagram. The unconditional probability P(A) = 0.30 + 0.10 + 0.12 = 0.52. However, the conditional probability P(A|B1) = 1, P(A|B2) = 0.12 ÷ (0.12 + 0.04) = 0.75, and P(A|B3) = 0.
On a tree diagram, branch probabilities are conditional on the event associated with the parent node. (Here, the overbars indicate that the event does not occur.)