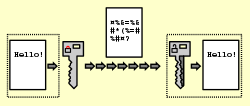
Encryption
Encryption allows information to be hidden so that it cannot be read without special knowledge (such as a password). This is done with a secret code or cypher. The hidden information is said to be encrypted.
Decryption is a way to change encrypted information back into plaintext. This is the decrypted form. The study of encryption is called cryptography. Cryptanalysis can be done by hand if the cypher is simple. Complex cyphers need a computer to search for possible keys. Decryption is a field of computer science and mathematics that looks at how difficult it is to break a cypher.
Examples
A simple kind of encryption for words is ROT13. In ROT13, letters of the alphabet are changed with each other using a simple pattern. For example, A changes to N, B changes to O, C changes to P, and so on. Each letter is "rotated" by 13 spaces. Using the ROT13 cipher, the words Simple English Wikipedia becomes Fvzcyr Ratyvfu Jvxvcrqvn. The ROT13 cipher is very easy to decrypt. Because there are 26 letters in the English alphabet, if a letter is rotated two times by 13 letters each time, the original letter will be obtained. So applying the ROT13 cipher a second time brings back the original text. When he communicated with his army, Julius Caesar sometimes used what is known as Caesar cipher today. This cipher works by shifting the position of letters: each letter is rotated by 3 positions.
Most kinds of encryption are made more complex so cryptanalysis will be difficult. Some are made only for text. Others are made for binary computer data like pictures and music. Today, many people use the asymmetric encryption system called RSA. Any computer file can be encrypted with RSA. AES is a common symmetric algorithm.
One-time pad
Most types of encryption can theoretically be cracked: an enemy might be able to decrypt a message without knowing the password, if he has clever mathematicians, powerful computers and lots of time. The one-time pad is special because, if it is used correctly, it is impossible to crack. There are three rules that must be followed:
- The secret key (password) must be as long as the secret message: if the message has 20 letters then the key must also have at least 20 letters.
- The secret key must be random (e.g. KQBWLDA...)
- The secret key must only be used once. To send more than one message, a different key must be used for each one.
If these three rules are obeyed, then it is impossible to read the secret message without knowing the secret key. For this reason, during the Cold War, embassies and large military units often used one-time pads to communicate secretly with their governments. They had little books ("pads") filled with random letters or random numbers. Each page from the pad could only be used once: this is why it is called a "one-time pad".
Encryption on the Internet
Encryption is often used on the Internet, as many web sites use it to protect private information. On the Internet, several encryption protocols are used, such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), IPsec, and SSH. They use the RSA encryption system and others. The protocol for protected web browsing is called HTTPS. URL encryption mostly uses the MD5 Algorithm. Various algorithms are used in the internet market depending upon the need.
Encryption Media
Related pages
- FreeOTFE - Disk encryption
- Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) - Email encryption
- PuTTY - SSH encryption