Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit (more precisely, a degree Fahrenheit) is a unit of measurement that is used to measure temperature. The conversion rate to degrees Celsius is C= 5/9 x (F − 32). The unit is abbreviated °F.
| Standard: | Imperial/US customary |
| Quantity: | Temperature |
| Symbol: | °F |
| Named after: | Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit |
History
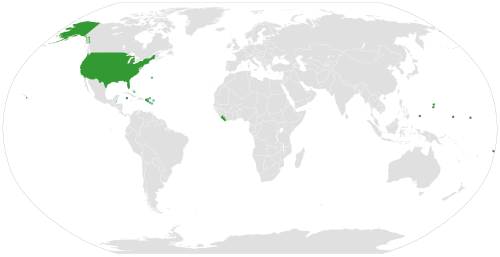
This temperature scale was made in 1724 by a German scientist named Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. In the 20th century, the unit became less used, and the degree Celsius more used. Fahrenheit is still often used in the United States. Fahrenheit is still used on some websites and on weather forecasts in the United Kingdom mainly since the older population is more familiar with it than with Celsius.
Fahrenheit is considered by many to be an old-fashioned and outdated way of measuring temperature and has been largely replaced with Celsius.
Overall, the use of Fahrenheit is in decline throughout most of the world, with the US being the main exception.
Examples
- Water freezes at 32 °F and boils at 212 °F.
- Room temperature is about 70 °F.
- A human's body temperature is usually close to 98.6 °F.
- Absolute zero is –459.67 °F.