File:Eunectes-murinus -Broghammerus-reticulatus- -Titanoboa-2.svg
Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 800 × 267 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 107 pixels | 640 × 213 pixels | 1,024 × 341 pixels | 1,280 × 427 pixels | 1,440 × 480 pixels.
Original file (SVG file, nominally 1,440 × 480 pixels, file size: 182 KB)
| This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. The description on its description page there is shown below.
|
Summary
| DescriptionEunectes-murinus -Broghammerus-reticulatus- -Titanoboa-2.svg |
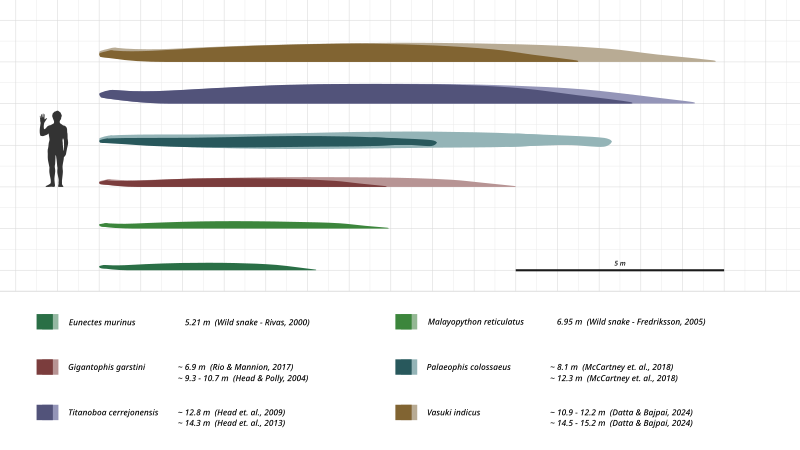
English: A size comparison of four different snakes; comparing large individuals of the extant green anaconda (Eunectes murinus) and reticulated python (Malayopython reticulatus) to total length estimates of the extinct Gigantophis and Titanoboa.
References
|
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | Gamma 124 |
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license:
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
Captions
Big snake
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
29 April 2018
image/svg+xml
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 03:55, 24 April 2019 | 1,440 × 480 (182 KB) | Steveoc 86 | Typo - 14.9 to 14.3 |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Width | 1440 |
|---|---|
| Height | 480 |