Hernia
A hernia is a medical condition. If an organ or its tissue moves from its normal position through to another position, it is called a hernia.
| Hernia | |
|---|---|
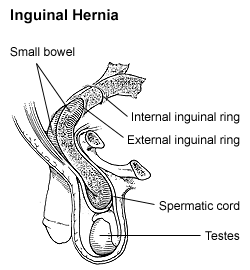 | |
| Diagram of an indirect inguinal hernia (view from the side) | |
| Symptoms | Pain especially with coughing, bulging area[1] |
| Complications | Bowel strangulation[1] |
| Usual onset | < 1 year and > 50 years old (groin hernias)[2] |
| Risk factors | Smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease, connective tissue disease[1][2][3] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, medical imaging[1] |
| Treatment | Observation, surgery[1] |
| Frequency | 18.5 million (2015)[4] |
| Deaths | 59,800 (2015)[5] |
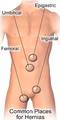
There are various types of hernia. Most hernias happen in the abdomen. Hernias sometimes give pain and/or a lump that can be felt or seen.
The cause can be hereditary or it can be from lifting objects, especially lifting ones that are too heavy, or if it is done in a wrong way. There are other things that can give hernias. Hernias, especially if small or mild, can be treated with medicine. But it will not go away from this treatment, although it will relieve symptoms.
Types of hernia
- Inguinal Hernia - Inguinal hernia occurs when a small portion of the intestine exits the inguinal canal and enters the femoral joint. Flatulence is a disorder of the esophagus, which usually involves the lining of the abdomen.[6]
- Femoral Hernia - This type of hernia develops when fatty tissue or part of the intestines sticks out of the groin at the top of the inner part of the thigh. It is comparatively less common than inguinal hernia and mainly affects women.[7]
- Umbilical Hernia - When a muscle or tissue hole opens near the umbilical cord, it starts coming out of the internal part of our body, it is called umbilical hernia. In umbilical hernia, there is swelling in the area around the navel.

Hernia treatments
Laparoscopic procedures for hernia repair
Laparoscopic, or minimally invasive, procedures use several small incisions to access the hernia no more than 1 centimeter in length. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide to provide space for the surgeon to work, and the hernia is repaired with a small, flexible instrument called a laparoscope.[8]
Open surgery
This is an open-cut surgery that is performed in the area of the hernia. In this procedure, the protruding tissues are set back, and the weak muscles are stitched up neatly. Also, these are times when a type of mesh will be inserted over the area to provide additional support.[9]
Reconstructive surgery for hernia repair
Abdominal wall reconstruction repairs defects in the abdominal walls while reducing abdominal tension and providing structural support. This may require a component separation so that the muscular sides of the hernia gap can be brought together again. There are many more than just a one type of a hernia.
Hernia Media
Inguinal hernia. By pushing on the hernia, it can be (reduced) pushed into the abdomen. When the pressure is removed, the hernia quickly reappears.
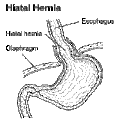
Diagram of a hiatus hernia (coronal section, viewed from the front).
Hernia repair being performed aboard the amphibious assault ship USS Bataan.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedNEJM15. - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedDom2014. - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedBMJ2014. - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedGBD2015Pre. - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedGBD2015De. - ↑ "Hernia: Types, Treatments, Symptoms, Causes & Prevention". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved 2021-11-22.
- ↑ "Hernia Symptoms in Women | Hernia in Women". Sahyadri Hospital. 2021-11-01. Retrieved 2021-11-22.
- ↑ Fisher, Martin. "Hernia Treatment Options | Comprehensive Hernia Center". www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2021-12-06. Retrieved 2021-12-06.
- ↑ "Hernia - Causes, Symptoms, Treatments | ONP Hospital | ONP Hospital". onphospitals.com. Retrieved 2021-12-06.