Lymph node
A Lymph node (IPA: [ lɪmf noʊd]) is an organ consisting of many types of cells, and is a part of the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and remove foreign (not of the body) objects from the body. Lymph nodes contain white blood cells. They are important for the correct use of the immune system.[1]
Location

In the human body, the most likely place where lymph nodes can be felt are the neck, underarms, and groin area.[1]
Lymph Node Media
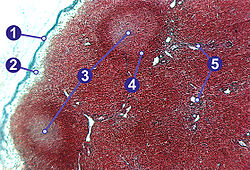
Cross-section of a lymph node with sections labelled.1) Capsule; 2) Subcapsular sinus; 3) Germinal center; 4) Lymphoid nodule; 5) Trabeculae
Histology of a normal lymphoid follicle, showing dark, light, mantle and marginal zones
Labeled diagram of human lymph node showing the flow of lymph
Diagram of a lymph node showing lymphocytes
Micrograph of a mesenteric lymph node with adenocarcinoma
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Lymph Node", TheLymphNodes.com, 2008, archived from the original on 2021-07-30, retrieved 2009-03-05