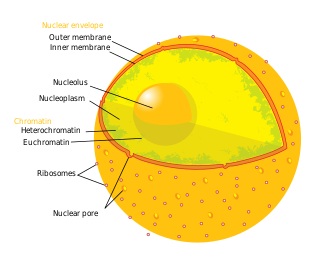
Nucleoplasm
Nucleoplasm is the contents of the cell nucleus. It is the protoplasm inside the nuclear membrane.
It includes
- many smaller molecules, and water
- large molecules such as enzymes of many types, and nucleotides
- larger organelles such as the chromosomes and the nucleoli
- A network of nucleolar channels makes a continuous chain between the nucleoplasm and the inner parts of the nucleolus. Ribosomes made in the nucleolus get sent to the endoplasmic reticulum in the cytoplasm.
The main role of the nucleoplasm is to keep the chromosomes separate from the cell cytoplasm, and support the translating of DNA to RNA
+{{{1}}}−{{{2}}}
Nucleoplasm Media
Polish-German botanist and namer of nucleoplasm, Eduard Strasburger.
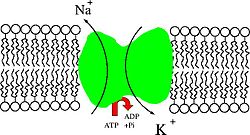
An example of the sodium-potassium pump, a P-type ATPase, which controls the ionic gradient across the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope as well as the ionic makeup of the nucleoplasm through the selective pumping of sodium and potassium ions.