Oxalate

Oxalate ion structure (the dotted or dashed lines means there is a resonance).
Oxalate (also known as ethanedioate) is a salt or ester of oxalic acid. It is also an ion of oxalic acid. It is a conjugate base of hydrogenoxalate. The chemical formula is C
2O2−
4 when it exists as an ion itself. It is formed when oxalic acid dissolves in water (which splits into an oxalate anion and two hydrons). Oxalate salts and esters are colourless.
Examples
- Sodium oxalate: Na
2C
2O
4 - Magnesium oxalate: MgC
2O
4 - Potassium oxalate: K
2C
2O
4 - Calcium oxalate: CaC
2O
4 - Dimethyl oxalate: (CH
3)
2C
2O
4 - Diethyl oxalate: (C
2H
5)
2C
2O
4
Oxalate Media
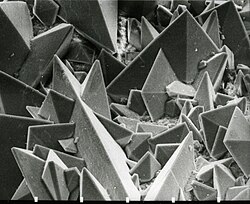
Scanning electron micrograph of the surface of a kidney stone showing tetragonal crystals of weddellite (calcium oxalate dihydrate) emerging from the amorphous central part of the stone; the horizontal length of the picture represents 0.5 mm of the figured original.
Related pages
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
+{{{1}}}−{{{2}}}