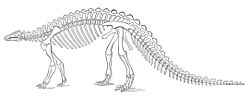
Scelidosaurus
Scelidosaurus was an early type of herbivorous dinosaur. It was a thyreophoran, a lightly plated, herbivorous dinosaur about 4 metres long. It lived during the early Jurassic, 196 to 183 million years ago. Its fossils were found in Charmouth, Dorset, England.[1]
| Scelidosaurus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scelidosaurus cast of the David Sole specimen, in Utah. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | Ornithischia |
| Clade: | Thyreophora |
| Clade: | Thyreophoroidea |
| Family: | Scelidosauridae |
| Genus: | Scelidosaurus Owen, 1859 |
| Species: | S. harrisonii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Scelidosaurus harrisonii Owen, 1861
| |
Scelidosaurus has been called the earliest complete dinosaur.[2]
It is one of the earliest and most basal of the armoured dinosaurs. A review by Serano had Scelidosaurus as the sister group (closest relative) to both the Stegosauria and Ankylosauria.[3]
This genus lived on the supercontinent Laurasia. Its length was about 4 metres (13 ft).[4] Scelidosaurus was quadrupedal, with the hindlimbs longer than the forelimbs. It may have reared up on its hind legs to browse on foliage from trees, but its forefeet were as large as its hind feet. This suggests a mostly quadrupedal posture.
Scelidosaurus and its Jurassic relatives were herbivorous. Other ornithischians had teeth capable of grinding plant material, but Scelidosaurus had smaller, less complex teeth. Its jaw could only do simple up-and-down movements.[4] In this aspect, they resembled the stegosaurids, which also had primitive teeth and simple jaws.[5] Also, like stegosaurs, they may have swallowed gastroliths to aid processing of food (because of the lack of chewing ability). This is also done by modern birds and crocodiles.[6] The diet of Scelidosaurus was low-lying plants like ferns and cycads.[4] Seaweed has also been suggested as a food. Grass did not evolve until the Cretaceous period.
Scelidosaurus Media
Cast of a nearly complete skeleton found in 2000 by David Sole, showing fossilised bony scutes, Charmouth Heritage Coast Centre
Life restoration showing bipedal posture, as indicated by a fossil trackway
NHMUK PV 39496, the first lectotype of Scelidosaurus, that proved to belong to a theropod, Dornraptor, instead
References
- ↑ BBC Family & Education. [1]
- ↑ Norman, David 2001. Scelidosaurus, the earliest complete dinosaur. In The armored dinosaurs, pp 3-24. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 0253339642
- ↑ Serano P.C. 1986. Phylogeny of the bird-hipped dinosaurs (Order Ornithischia). National Geographic Research 2, 234–256.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lambert D 1993. The ultimate dinosaur book. Dorling Kindersley, New York, p110-113. ISBN 1-56458-304-X
- ↑ Galton PM, Upchurch P (2004). "Stegosauria". In Weishampel DB, Dodson P, Osmólska H (ed.). The Dinosauria (2nd Edition. University of California Press. p. 361. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ↑ Stegosaurs Archived 2012-06-29 at Archive.today Jacobson RJ. Dinosaur and vertebrate paleontology information. Retrieved 2007-02-11.