Voice over Internet Protocol
Voice over Internet protocol (or VoIP) is a term used for a number of protocols that are used to carry voice data over packet switched networks. Before, telephony used a dedicated line that was only for calls. This was known as PSTN (or "public switched telephony network"). Using VoIP will reduce costs, as the "dedicated line" for telephony (and fax) is no longer needed.[1][2]
There are a number of technical problems that must be solved first, though:
- Carrying voice data needs service guarantees (mostly in the form of "throughput", and "response time"). Not having this will result in a loss of signal (or in "hiccups")
- Most telephony networks provide the possibility to operate a phone, even when the power is lost in the area. This is done so that emergency calls can still be made. VOIP usually does not provide this possibility.
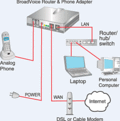
- The LAN is now used both for voice and data, and becomes a single point of failure. If there are problems with the LAN, this can also affect VOIP calls.
- The encoding schemes used for voice calls are not good choices for fax or other uses of the telephony network.
The vast majority of VoIP systems rely on two main protocols:[3]
SIP :- SIP, or also known as session initiation protocol, has become the standard for multimedia sessions on the internet. The Engineering Task Force thinks of this protocol as the standard for audio, video and even instant messaging solutions. This task force is simply a large, international community, composed of anyone involved in the networking evolution online. SIP is modular, meaning that it can be changed around in whatever way needed. Depending on the type of data your business is wishing to transmit, your SIP deployment will need to be designed specifically for this. With that being said, VoIP and IM communications will need to work around these aspects, and be designed for one total approach.
H.323 :- This protocol has become the international standard for all communication over packet-switched networks. This includes LAN, WAN and even the general internet networks we all connect to. H.323 is considered an umbrella that includes all types of standards, which is what the internet is based on. H.323 focuses on voice, video, and data communications, designed specifically to operate over IP networks. At this point, this protocol has become the world market leader for voice and voice communications over IP networks. H.323 was developed by the international telecommunications union, which is the organization responsible for building the public telephone network.
Voice Over Internet Protocol Media
Asterisk-based PBX for small business
References
- ↑ "Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP)". Federal Communications Commission. 2010-11-18. Archived from the original on 2023-10-20. Retrieved 2021-06-15.
- ↑ "VoIP: how it can help your business". PWR Technologies. 2021-11-01. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
- ↑ "Understanding VoIP Protocols". Nirvanix. Archived from the original on 2021-06-16. Retrieved 2021-06-15.