Angular velocity
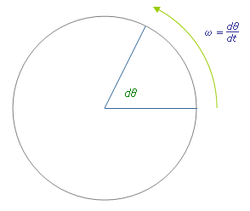
In physics, the angular velocity specifies the angular speed at which an object is rotating along with the direction in which it is rotating.
It is a vector quantity.[1] The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second. But it may be measured in other units as well (such as degrees per second, degrees per hour, etc.). When it is measured in cycles or rotations per unit time (e.g. revolutions per minute), it is often called the rotational velocity and its magnitude the rotational speed. Angular velocity is usually represented by the symbol omega (Ω or ω). The direction of the angular velocity vector is perpendicular to the plane of rotation, in a direction which is usually specified by the right hand rule.
Angular Velocity Media
The angular velocity of the particle at P with respect to the origin O is determined by the perpendicular component of the velocity vector v.
Related pages
References
- ↑ more precisely, a pseudovector
- Symon, Keith (1971). Mechanics. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA. ISBN 0-201-07392-7.
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. (1997). Mechanics. Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-750-62896-0.



