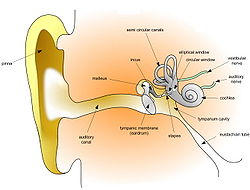
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense for hearing. The sense organ for hearing is the ear.
Structure of the ear
Outer ear
The outer ear is the folds of cartilage surrounding the ear canal. They are called the pinna.
Middle ear
Sound waves travelling through the ear canal will hit the tympanum, or eardrum. Three tiny bones, the ossicles, convert the waves to high pressure vibrations. They are then converted to nerve impulses in the cochlea.
Inner ear
The inner ear is made mostly of the cochlea. The cochlea is made up of three pieces, and is filled with liquid. It transforms sound waves to electric signals in neurons. The semicircular canals of the inner ear are used in equilibrioception, the sense of balance.
Auditory System Media
This animated video illustrates how sounds travel to the inner ear, and then to the brain, where they are interpreted and understood. The cochlea in the inner ear is a spiral-shaped organ that contains hair cells, which sense sound vibrations. Hair cells convert sound vibrations into chemical signals that the auditory nerve can understand.
Anatomy of the human ear (The length of the auditory canal is exaggerated in this image.).Template:Anatomy of the human ear - color legend
The organ of Corti located at the scala media
Lateral lemniscus in red, as it connects the cochlear nucleus, superior olivary nucleus and the inferior colliculus, seen from behind
Related pages
Other websites
- Promenade 'round the cochlea Archived 2007-08-27 at the Wayback Machine
- Washington University Neuroscience Tutorial - Auditory system Archived 2006-02-05 at the Wayback Machine