Autofocus
Autofocus is a procedure for finding the correct position of the lens for a scene. The autofocus feature can be provided in a system which includes a movable optical element, a motor, an image sensor and a processing unit. The autofocus procedure is done by changing the lense position and image quality measurements in each position. The position that provides the image with the best quality will be used as the best focus.
The image quality may be estimated using image gradients. To speed-up the autofocus procedure, the autofocus is done in two steps: the first run over the full range of the lenses movement with a significant step will provide the estimated position which will be improved in the second run over the small range with a small step. Interpolation between the few best positions may improve the results accuracy.
Autofocus Media
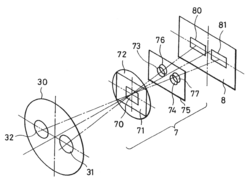
Phase detection system:*7 – Optical system for focus detection;*8 – Image sensor;*30 – Plane of the vicinity of the exit pupil of the optical system for photography;*31, 32 – Pair of regions;*70 – Window;*71 – Visual field mask;*72 – Condenser lens;*73, 74 – Pair of apertures;*75 – Aperture mask;*76, 77 – Pair of reconverging lenses;*80, 81 – Pair of light receiving sections
Active autofocus system via infrared - Canon AF35M (1979)
Early passive autofocus system integrated in the lens with Pentax ME-F (1981)
Modern (2014) autofocus single lens reflex camera - Nikon D4
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |