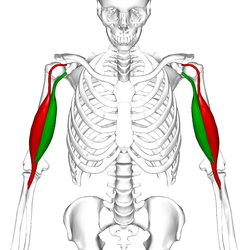
Biceps
The biceps, also called the biceps brachii, is a muscle in the arm. It has two parts, a long part and a short part. Using the elbow the muscle helps the movement of the forearm. When the muscle shortens, it bends the elbow and twists the forearm so that the palm faces up. The two parts of the muscle start on different parts of the shoulder blade and end together on the forearm.[1]
The biceps is also a muscle in other quadrupeds. In humans, the muscle is more complex, and allows more complex movement than in other quadrupeds.
The word biceps literally means two-headed, and refers to the fact that the muscle attaches to two different parts of the shoulder. In quadrupeds, the muscle only attaches at one point of the shoulder.
Biceps Media
Panoramic ultrasonography of a proximal biceps tendon rupture. Top image shows the contralateral normal side, and lower image shows a retracted muscle, with a hematoma filling out the proximal space.
Biceps and triceps.
References
- ↑ Lippert, Lynn S. (2006). Clinical kinesiology and anatomy (4th ed.). Philadelphia: F. A. Davis Company. pp. 126–7. ISBN 978-0-8036-1243-3.
+{{{1}}}−{{{2}}}