Breadth-first search
In computer science, breadth-first search (BFS) is a method used for traversing a graph. It starts at any item you want to use as a starting position in a graph, and explores all of the neighbor items at the present depth before to moving on to the items at the next depth level. A breadth-first search done on a tree (data structure) is called a level-order traversal.
Implementation
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> void breadthFirstSearch(Item root) {
Queue q = new Queue();
root.found = true;
q.enqueue(item);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Item v = q.dequeue();
for (Item neighbor : v.neighbors()) {
if (!neighbor.found) {
neighbor.found = true;
q.enqueue(neighbor);
}
}
}
} </syntaxhighlight>
Usage
Though they have usage in a variety of disciplines, breadth first search algorithms are most often associated with finding the shortest distance between two points, such as on a map.
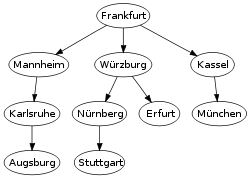
Breadth-first Search Media
BFS on Maze-solving algorithm
Top part of Tic-tac-toe game tree
An example map of Southern Germany with some connections between cities
The breadth-first tree obtained when running BFS on the given map and starting in Frankfurt