Brittany
Brittany (French: Bretagne, Breton: Breizh) is a region in Northwest France. The adjective for Brittany is Breton.
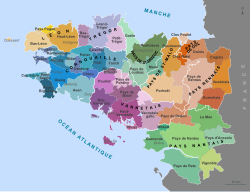
Today the official administrative region has 4 departments:
Before 1941, a fifth département was part of Brittany: Loire-Atlantique, which includes Nantes. The five departments form the cultural region of Brittany, also known as "historical Brittany".
Brittany is in the western France and its coastline points out into the Atlantic. Warmed by the Gulf Stream, Brittany has a mild and temperate climate with warm summers and wet winters.
Three languages are traditionally spoken in Brittany:
- Breton language in the West part, a Celtic mix similar to Cornish;
- Gallo (a Romance language) in the East part;
- And everywhere, French.
The capital of Brittany is Rennes in the Ille-et-Vilaine department.
The name of Brittany is related to Great Britain (in French, Grand Bretagne). The region has also been called Lesser Britain or Little Britain in the past. After the Anglo-Saxons started arriving in Great Britain in the 5th century, many of the Ancient Britons (Celts) moved to this region. The region may have already had strong ties with the Ancient Britons even before that. These tribes gave Brittany its name, the Breton language, the local place names and many parts of its culture. Brittany was a separate country from the 9th century until it was united with France in 1532. It was a province of France until the French Revolution, when its land was divided in departments. Brittany regained a regional government in the 1980s.
Brittany is the home of the world's largest collection of standing stones in one place, the Carnac stones.
Brittany's main industry is agriculture, in particular: pork farming, chicken farming and the production of maize (for cattle feed). Brittany is also the name of a dog breed.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
Brittany Media
A recording by the arranger of this piano version of Hen Wlad fy Nhadau, the Welsh national anthem.
The temple of Mars in Corseul
A French map of the traditional regions of Brittany in Ancien Régime France. The earlier state of Domnonia or Domnonée that united Brittany comprised the counties along the north coast
The Brythonic community around the 6th century. The sea was a communication medium rather than a barrier.
Anne of Brittany is regarded in Brittany as a conscientious ruler who defended the duchy against France.
Province of Brittany (1789) – showing internal borders of five new departments: Côtes-du-Nord (now Côtes-d'Armor), Finistère, Ille-et-Vilaine, Loire-Inférieure (now Loire-Atlantique) and Morbihan.
A Breton speaker, recorded in Canada.