Cartesian product
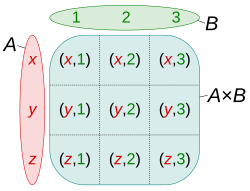
In mathematics, sets can be used to make new sets. Given two sets A and B, the Cartesian product of A with B is written as A × B,[1] and is the set of all ordered pairs whose first element is a member of A, and whose second element is a member of B.[2]
For example, let A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {a, b}. Then:
- [math]\displaystyle{ A \times B = \{(1, a), (1, b), (2, a), (2, b), (3, a), (3, b)\} }[/math]
The set of a Cartesian product can be visualized as a two-dimensional table, with its entry being its elements.[3]
Cartesian Product Media
Related pages
References
- ↑ "Comprehensive List of Set Theory Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-04-11. Retrieved 2020-09-05.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Cartesian Product". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-09-05.
- ↑ "Cartesian Product". web.mnstate.edu. Archived from the original on 2020-07-18. Retrieved 2020-09-05.