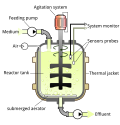
Cultured meat
Cultured meat, also called cultivated meat,[1] is meat grown in cell culture instead of inside animals.[2] It is a form of cellular agriculture. Cultured meat is produced using many of the same tissue engineering techniques used in regenerative medicine.[3] Until now, the cost to produce cultured meat has been extremely high.[4] The first cultured burger patty, created by Dr. Mark Post at Maastricht University, was eaten in August 2013, at a demonstration for the press in London.[5]
Cultured meat is believed to be something that can help solve concerns about the environment,[6] animal welfare, food security, and human health.[7][8][9][10][11][12][13]
Cultured Meat Media
Mark Post of the University of Maastricht presents The Meat Revolution, a lecture about cultured meat, 2015
Isha Datar of New Harvest on how a "post-animal bio-economy" can be brought about through cultured meat, eggs, and milk, 2017
Bioprinting that assembles cell fibers could be used to produce a variety of steak-like cultured meat.
References
- ↑ Malerich, Marlana; Bryant, Christopher (2022). "Nomenclature of cell-cultivated meat & seafood products". npj Science of Food. 6 (1): 56. doi:10.1038/s41538-022-00172-0. PMC 9734853. PMID 36496502.
- ↑ Verbeke, Wim (February 2015). "Challenges and prospects for consumer acceptance of cultured meat". Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 14 (2): 285–294. doi:10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60884-4. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- ↑ Post, Mark (4 December 2013). "Medical technology to Produce Food". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 94 (6): 1039–1041. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6474. PMID 24214798. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "The $325,000 Lab-Grown Hamburger Now Costs Less Than $12". Fast Company. April 2015. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ↑ "World's first lab-grown burger is eaten in London". BBC News. 5 August 2013. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-23576143. Retrieved 2 February 2016.
- ↑ De Lorenzo, Daniela (17 March 2022). "Dutch Parliament Approves Cultured Meat Tasting In The Netherlands". Forbes.com. https://www.forbes.com/sites/danieladelorenzo/2022/03/17/dutch-parliament-approves-cultured-meat-tasting-within-the-netherlands/?sh=274e269460bf. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ↑ Gaydhane, Mrunalini K.; Mahanta, Urbashi; Sharma, Chandra S.; Khandelwal, Mudrika; Ramakrishna, Seeram (2018). "Cultured meat: state of the art and future". Biomanufacturing Reviews. 3 (1). doi:10.1007/s40898-018-0005-1.
- ↑ Post, Mark J.; Levenberg, Shulamit; Kaplan, David L.; Genovese, Nicholas; Fu, Jianan; Bryant, Christopher J.; Negowetti, Nicole; Verzijden, Karin; Moutsatsou, Panagiota (2020). "Scientific, sustainability and regulatory challenges of cultured meat". Nature Food. 1 (7): 403–415. doi:10.1038/s43016-020-0112-z. Archived from the original on 13 May 2024. Retrieved 8 April 2024.
- ↑ Bryant, Christopher J (2020). "Culture, meat, and cultured meat". Journal of Animal Science. 98 (8): skaa172. doi:10.1093/jas/skaa172. ISSN 0021-8812. PMC 7398566. PMID 32745186.
- ↑ Hong, Tae Kyung; Shin, Dong-Min; Choi, Joonhyuk; Do, Jeong Tae; Han, Sung Gu (2021). "Current Issues and Technical Advances in Cultured Meat Production: AReview". Food Science of Animal Resources. 41 (3): 355–372. doi:10.5851/kosfa.2021.e14. ISSN 2636-0772. PMC 8112310. PMID 34017947.
- ↑ Treich, Nicolas (2021). "Cultured Meat: Promises and Challenges". Environmental and Resource Economics. 79 (1): 33–61. Bibcode:2021EnREc..79...33T. doi:10.1007/s10640-021-00551-3. ISSN 1573-1502. PMC 7977488. PMID 33758465.
- ↑ Chriki, Sghaier; Ellies-Oury, Marie-Pierre; Hocquette, Jean-François (2022). "Is "cultured meat" a viable alternative to slaughtering animals and a good comprise between animal welfare and human expectations?". Animal Frontiers. 12 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1093/af/vfac002. PMC 8929989. PMID 35311183.
- ↑ Chen, Lu; Guttieres, Donovan; Koenigsberg, Andrea; Barone, Paul W.; Sinskey, Anthony J.; Springs, Stacy L. (2022). "Large-scale cultured meat production: Trends, challenges and promising biomanufacturing technologies". Biomaterials. 280: 121274. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121274. PMID 34871881.