Food security
Food security means that everyone in a specific geographical area has access to food. This also means that the food is affordable. That way everyone in the area can get enough food for a varied diet, with enough nutrients. This is especially important for staple food. If there's no food security, malnutrition and famine will result. People who cannot get enough food will also be more likely to start riots.
If there is no food security, this is called food insecurity. One of the reasons for food insecurity is that there are special markets (like stock markets) for food (called commodities). Like with other goods, supply and demand influence the price. Grains can also be used as a food for livestock, or the can be processed to produce biofuel. These resources are then no longer directly available as food. People can place a bet on rising (or falling prices), something that is called a future. External events, such as bad harvests, or wars also influence the price.
Food insecurity can also be defined as the limitation or unavailability of nutritionally adequate food or the inability to acquire acceptable foods.[1]
Food Security Media
A Kenyan woman farmer at work in the Mount Kenya region
Bengali famine of 1943: The Japanese conquest of Burma cut off India's main supply of rice imports.
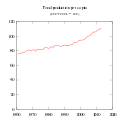
Growth in food production has been greater than population growth. Food per person increased since 1961. Data source: Food and Agriculture Organization.
Related pages
Other Sources for Information
References
- ↑ (PDF). 2013-11-04 https://web.archive.org/web/20131104185458/http://www.fns.usda.gov/fsec/files/fsguide.pdf. Archived from the original on 2013-11-04. Retrieved 2023-03-15.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)