Ethylene glycol
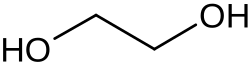
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2OH)2. It is used to make polyester and to make antifreeze.[4]
| Ethylene glycol | |
|---|---|
| |
| File:Samlpe of Ethylene glycol.jpg | |
Ethane-1,2-diol | |
| Other names | Ethylene glycol 1,2-Ethanediol Ethylene alcohol Hypodicarbonous acid Monoethylene glycol 1,2-Dihydroxyethane |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | MEG |
| CAS number | |
| PubChem | |
| EC number | 203-473-3 |
| KEGG | C01380 |
| MeSH | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:30742 |
| RTECS number | KW2975000 |
| SMILES | C(CO)O |
| Beilstein Reference | 505945 |
| Gmelin Reference | 943 |
| 3DMet | B00278 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C2H6O2 |
| Molar mass | 62.06 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Odorless[1] |
| Density | 1.1132 g/cm3 |
| Melting point |
−12.9 °C, 260 K, 9 °F |
| Boiling point | |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| Solubility | Soluble in most organic solvents |
| log P | -1.69[2] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.06 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
| Viscosity | 1.61×10−2 Pa·s[3] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| Explosive limits | 3.2–15.2%[1] |
| U.S. Permissible exposure limit (PEL) |
None[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Ethylene Glycol Media
Ethylene glycol is one precursor to polyethyleneterephthalate, which is produced on the multimillion ton scale annually.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0272". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Ethylene glycol". www.chemsrc.com.
- ↑ Elert, Glenn. "Viscosity". The Physics Hypertextbook. Retrieved 2007-10-02.
- ↑ Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Identifiers at line 630: attempt to index field 'known_free_doi_registrants_t' (a nil value).

