Viscosity
Viscosity is a physical property of fluids. It shows resistance to flow.[1] In a simple example, water has a low viscosity, as it is "thin". Syrup and tar, on the other hand, have a high viscosity, as they are "thick". A way to test for viscosity is the speed at which the substance runs down a slope. Syrup would reach the bottom very slowly, and water would be much quicker.
There are two types of viscosity: dynamic viscosity, measured in pascal seconds, and kinematic viscosity, measured in metres squared per second .[2]
Viscosity is used as a way to predict when volcanoes erupt. When the lava comes out very thickly (viscous), there is more chance that it will erupt violently. This is because the lava has a hard time getting out and may burst out when it can. If the lava is thin (low viscosity), then it just flows out like water.[3]
The word viscous comes from the Latin root viscum, meaning sticky.[4]
Viscosity Media
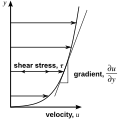
Illustration of a planar Couette flow. Since the shearing flow is opposed by friction between adjacent layers of fluid (which are in relative motion), a force is required to sustain the motion of the upper plate. The relative strength of this force is a measure of the fluid's viscosity.
Video showing three liquids with different viscosities
Experiment showing the behavior of a viscous fluid with blue dye for visibility
Common logarithm of viscosity against temperature for B2O3, showing two regimes
In the University of Queensland pitch drop experiment, pitch has been dripping slowly through a funnel since 1927, at a rate of one drop roughly every decade. In this way the viscosity of pitch has been determined to be approximately 230 billion (2.3×1011) times that of water.[6]
References
- ↑ Elert, Glenn (2021). "Viscosity". The Physics Hypertextbook.
- ↑ "Quantities and Units of Viscosity". Uniteasy.
- ↑ "What is Viscosity? (with pictures)". wiseGEEK.
- ↑ "viscous - Origin and meaning of viscous". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ↑ Fluegel 2007.
- ↑ Edgeworth, Dalton & Parnell 1984, pp. 198–200.