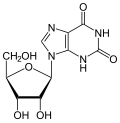
Nucleobase
A nucleobase is a part of RNA and DNA which may be involved in pairing (see base pair). Nucleobases are important for genetics.
They include cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine in (DNA), uracil in (RNA) and xanthine and hypoxanthine (mutated forms of guanine and adenine). These are abbreviated as C, G, A, T, U, X and HX respectively. They are usually simply called bases in genetics. Because A, G, C and T appear in the DNA, these molecules are called DNA-bases; A, G, C and U are called RNA-bases.
Uracil replaces thymine in RNA.
Nucleobase Media
Base pairing: Two base pairs are produced by four nucleotide monomers, nucleobases are in blue. Guanine (G) is paired with cytosine (C) via three hydrogen bonds, in red. Adenine (A) is paired with uracil (U) via two hydrogen bonds, in red.
Other websites
- Base pairing in DNA Double Helix (shows specific hydrogen bonds) Archived 2006-06-21 at the Wayback Machine