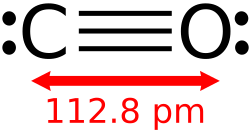Oxide
(Redirected from Oxides)
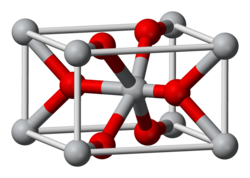
An oxide is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and at least one atom of one other element. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides (mainly silica). Oxides can be made when elements are oxidized by air (when oxygen in the air reacts with the element).
Some common oxides are:
- Water (hydrogen oxide) (H2O)
- Iron(III) oxide (Rust) (Fe2O3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Lead(II) oxide (PbO)
- Calcium oxide (CaO)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Magnesium oxide (Magnesia) (MgO)
- Phosphorus pentoxide (P4O10)
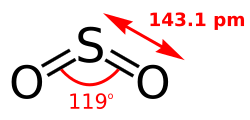
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Sulfur trioxide (SO3)
- Silicon dioxide (SiO2)
- Nitrous oxide (laughing gas) (N2O)
- Zinc oxide (ZnO)
- Copper(I) oxide (CuO) and Copper(II) oxide (Cu2O)
Oxide Media
Carbon dioxide is the main product of fossil fuel combustion.
Carbon monoxide is the product of the incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels and a precursor to many useful chemicals.
Nitrogen dioxide is a problematic pollutant from internal combustion engines.
Sulfur dioxide, the principal oxide of sulfur, is emitted from volcanoes.
Nitrous oxide ("laughing gas") is a potent greenhouse gas produced by soil bacteria.