Phosphate
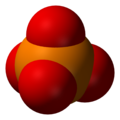
A phosphate is a salt of phosphoric acid. Phosphates are important in biochemistry. Phosphates have the formula PO43- and a molar mass of 94.973 g/mol. An example of a phosphate is sodium phosphate. Three different types of phosphates are known. They are orthophosphate, PO43-; metaphosphate, PO32-; and pyrophosphate, P2O73-. They have a combining power of 3.
| Phosphate | |
|---|---|

| |
Phosphate[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| PubChem | |
| MeSH | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:18367 |
| SMILES | [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O |
| Beilstein Reference | 3903772 |
| Gmelin Reference | 1997 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | PO3− 4 |
| Molar mass | 94.9714 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Structure
Phosphates are made of one phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. Many phosphates do not dissolve in water.
Phosphate Media
Phosphoric acid speciation
Phosphate mine near Flaming Gorge, Utah, US, 2008
Train loaded with phosphate rock, Métlaoui, Tunisia, 2012
Sea surface phosphate from the World Ocean Atlas
Relationship of phosphate to nitrate uptake for photosynthesis in various regions of the ocean. Note that nitrate is more often limiting than phosphate. See the Redfield ratio.
H3PO4Phosphoricacid
[H2PO4]−Dihydrogenphosphate
[HPO4]2−Hydrogenphosphate
Sources
- ↑ "Phosphates – PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center of Biotechnology Information.