Torus
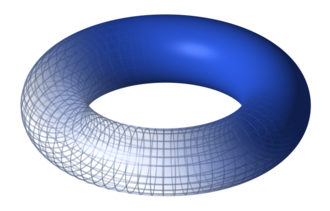
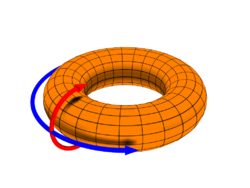
A torus (plural: tori or toruses) is a tube shape that looks like a doughnut or an inner tube. In geometry, a torus is made by rotating a circle in three dimensional space. To make a torus, the circle is rotated around a line (called the axis of rotation) that is in the same plane as the circle. Usually, the line does not touch the circle, so the torus has a hole through the center, and the torus is called a ring torus. For a ring torus, the axis of rotation passes through the center of the hole.
In topology, sizes don't matter, and a torus is any shape that has one hole through it.
The ring torus is the most well-known type of torus, but other types exist. If the line the circle rotates around is tangent to the circle, then it becomes a horn torus, and if it passes through the circle then it is a spindle torus. A toroid is a surface made by rotating any shape around a line, so a torus is one kind of toroid.
If the torus is filled to make a solid shape, it is called a solid torus. A solid torus is often simply called a torus. A solid torus is made by rotating a disk (a filled-in circle) around a line. Common objects that have the shape of a solid torus are a doughnut, a bagel and an O-ring. A ringette ring is torus-shaped.
A torus is like a tube that is bent into a circle so it connects to itself. The radius of the tube or circle is called the minor radius, written as [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math]. The distance from the center of the tube to the center of the torus is called the major radius, written as [math]\displaystyle{ R }[/math].
The surface area of a torus is given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} A &= \left( 2\pi r \right) \left(2 \pi R \right) = 4 \pi^2 R r \end{align} }[/math].
This area is the same as the area of a straight tube that has a radius [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] and length [math]\displaystyle{ 2\pi R }[/math].
The volume of a solid torus is given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} V &= \left ( \pi r ^2 \right ) \left( 2 \pi R \right) = 2 \pi^2 R r^2 \end{align} }[/math].
This volume is the same as the volume of a straight rod that has a radius [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] and length [math]\displaystyle{ 2\pi R }[/math].
Torus Media
As the distance from the axis of revolution decreases, the ring torus becomes a horn torus, then a spindle torus, and finally degenerates into a double-covered sphere.
A stereographic projection of a Clifford torus in four dimensions performing a simple rotation through the xz-plane
The configuration space of 2 not necessarily distinct points on the circle is the orbifold quotient of the 2-torus, T2 / S2, which is the Möbius strip.
- The Tonnetz is an example of a torus in music theory.The Tonnetz is only truly a torus if enharmonic equivalence is assumed, so that the (F♯-A♯) segment of the right edge of the repeated parallelogram is identified with the (G♭-B♭) segment of the left edge.
Seen in stereographic projection, a 4D flat torus can be projected into 3-dimensions and rotated on a fixed axis.