Water cycle
The water cycle, or hydrological cycle, is the cycle that water goes through on Earth.[1]
Overview
Water is essential for life as we know it. It is present throughout the Solar System, and was part of the Earth from its formation. The source of the water was the same as the source of the Earth's rock: the cloud particles which condensed in the origin of the Solar System.[2]
Processes
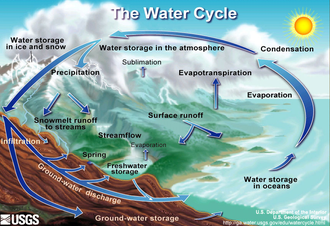
This is the process that water starts and ends in the water cycle.
- The cycle starts when water on the surface of the Earth evaporates. Evaporation means the sun heats the water which turns into a gas
- Then, water gathers as water vapour in the sky. This makes clouds
- Next, the water in the clouds gets cold. This makes it become liquid again. This process is called condensation
- Then, the water falls from the sky as rain, snow, sleet or hail. This is called precipitation
- The water sinks into the surface and also collects into lakes, oceans, or aquifers. It evaporates again and continues the cycle
- This whole process in which water evaporate and falls on the land and later flows back in river and pond is known as water cycle
Human activities affecting water cycle
- Industry
- Agriculture
- Deforestation
- Dam construction
- Removing groundwater from wells
- Taking water from rivers
Water Cycle Media
A detailed diagram depicting the global water cycle. The direction of movement of water between reservoirs tends towards upwards movement through evapotranspiration and downward movement through gravity. The diagram also shows how human water use impacts where water is stored and how it moves.
Video of the Earth's water cycle (NASA)
Relationship between impervious surfaces and surface runoff
Extreme weather (heavy rains, droughts, heat waves) is one consequence of a changing water cycle due to global warming. These events will be progressively more common as the Earth warms more and more.: Script error: The function "hyphen2dash" does not exist. 
Predicted changes in average soil moisture for a scenario of 2°C global warming. This can disrupt agriculture and ecosystems. A reduction in soil moisture by one standard deviation means that average soil moisture will approximately match the ninth driest year between 1850 and 1900 at that location.
Related pages
References
- ↑ "The Water Cycle". Dr. Art's Guide to Planet Earth. Archived from the original on 2011-12-26. Retrieved 2006-10-24.Water cycle. [1]
- ↑ Van Andel, Tjeerd H. 1994. New views on an old planet: a history of global change Chapter 14. 2nd ed, Cambridge. ISBN 0-521-44755-0