World Wide Web
| Internet |
|---|
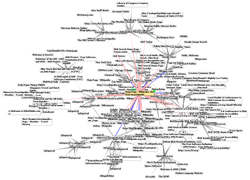
An Opte Project visualization of routing paths through a portion of the Internet |
|
|
- "The Web" redirects here. For other uses, see Web (disambiguation).
The World Wide Web ("WWW" or "The Web") is the part of the Internet that contains websites and webpages. It was invented in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN, Geneva, Switzerland. Sir Tim Berners-Lee created a new markup language called HTML. Each Website is a group of pages linked by hypertext links that are written in HTML.
The software to see the World Wide Web is called a web browser. To access the World Wide Web, one also needs a connection to the Internet.
Many companies nowadays offer website hosting allowing one to make websites that can be displayed on the World Wide Web, including a custom domain (www.stuff.com) site.
History

The World Wide Web was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 while he was working at CERN, a research center in Switzerland. He wanted to help scientists share documents and information easily over the Internet. He suggested a system using hypertext, which lets people click on links to move between documents.[1]
In 1990, Berners-Lee made the first version of the Web. It included:
- The first web browser and editor, called WorldWideWeb,
- The first web server, and
- The first web page, which explained what the Web was and how to use it.[2][3][4]
In 1991, the Web became available to researchers outside CERN. By 1993, it began to grow fast. That year, the Mosaic browser was released. It was the first popular browser with graphics, which made the Web easier to use and helped it spread worldwide.[5][6]
In 1994, Berners-Lee started the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) at MIT to create standards that would keep the Web open and accessible for everyone.[7]
Over time, the Web changed:
- In the 2000s, websites became more interactive with JavaScript, CSS, and AJAX, leading to what's called Web 2.0.
- Social media, online shopping, video streaming, and mobile sites became common.
- Recently, the Semantic Web, AI, and decentralized web ideas have started shaping the Web's future.[8][9]
Function
The World Wide Web works by combining several technologies so people can view and interact with content on the Internet.
When someone opens a website using a web browser, the browser sends a request to a web server asking for a web page. The server then sends the content back to the browser. This content is usually written in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which describes the structure of the page.[10]
Web pages can also include:
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), which control the design and layout of the page,[11]
- and JavaScript, which adds interactivity and lets the page respond to user actions.[12]
Web pages are connected to each other using hyperlinks. Clicking on a link tells the browser to open a new page.
Most websites use a client–server model:
- The browser (the "client") sends requests to the server.
- The server sends back the data needed for the page.[13]
These messages are usually sent using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or its secure version, HTTPS.[14]
Some websites also get extra content from other servers, like ads, videos, or social media tools. Many modern websites use dynamic content, which lets them update part of the page without needing to reload everything.[15]
Security and privacy
The Web uses several technologies to protect users and their data.
HTTPS encryption and authentication
Most websites use HTTPS, which adds the TLS encryption layer on top of HTTP. This keeps data like passwords and personal information safe from eavesdropping and tampering. HTTPS also lets browsers verify a site’s identity using digital certificates, and ensures the content isn’t changed in transit.[16][17]
Modern browsers block certain sensitive features unless the page is delivered via HTTPS. They also enforce security features like HSTS, certificate transparency, and improved cipher suites.[17]
Tracking and privacy risks
Websites may collect user data such as:
- IP addresses, used for basic connection purposes and limited location inference;
- HTTP cookies, which help websites remember users or track their activity.[18] Third-party cookies in particular can follow users across sites.[19]
Browsers and privacy tools increasingly block third-party cookies and tracking scripts by default.[20]
Example: Wikipedia's approach
Wikipedia shows how a large, community-run site balances openness and privacy:
- Anonymous editing is allowed; these edits show the user’s IP address.[21][22]
- Basic logs (IP, timestamps) are kept temporarily for site maintenance and then deleted; some logs remain public for accountability.[23][24]
- HTTPS is used everywhere, protecting all page views and edits since 2015.[25]
- The Wikimedia Foundation implements standard security practices, including encryption, firewalls, and secure data retention.[26]
Components
The Web consists of several key components that work together to display and interact with content online.
Web browsers
A web browser (such as Chrome, Firefox, Edge or Safari) requests web pages from servers, renders HTML/CSS/JavaScript, and provides tools like bookmarks, history, cookies, form support, and security features.[27][28]
Web servers
A web server is a computer (with server software like Apache, Nginx, CERN httpd) that listens for HTTP/HTTPS requests and returns web content—HTML, images, CSS, JavaScript. Servers can also generate pages dynamically using scripting languages.[28]
Web pages and HTML
- Web pages are documents written in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which defines elements like headings, paragraphs, images, and links.[29]
CSS and JavaScript
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) controls page appearance—layout, fonts, colors.
- JavaScript adds interactivity and enables dynamic behavior on the client side.[30]
URLs, HTTP/HTTPS and hyperlinks
- Each resource has a URL or URI that uniquely identifies it.
- The browser and server exchange data using HTTP or HTTPS.
- Hyperlinks connect pages, allowing users to navigate across the Web.
Web platform and Web Components
- The Web platform refers to open standards like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and APIs maintained by the W3C and other groups.[31]
- Web Components let developers create custom HTML elements with their own encapsulated structure, styling (Shadow DOM), and behavior (via JavaScript). They're supported in modern browsers.
Architecture and protocols
The architecture of the Web defines how its parts fit together—from clients and servers to protocols and addressing systems.
Client–server model
The Web uses a client–server model: a web browser (client) sends requests to a web server, which then delivers content such as HTML pages, images, CSS, and JavaScript back to the client. Requests and responses typically travel over an Internet network, often using separate machines for client and server.[32][33]
Resource identification (URIs/URLs)
Each resource on the Web—like a page, image, or video—is uniquely identified by a URI (or URL). These identifiers let browsers locate and request resources.[34]
HTTP and HTTPS
- The HTTP protocol, developed in 1990, defines how browsers ask for resources (with methods like GET and POST) and how servers respond.[35]
- HTTPS adds TLS (formerly SSL) encryption on top of HTTP. It protects data in transit, verifies server identity, and prevents tampering or eavesdropping.[36]
These protocols run over the **TCP/IP** suite, which ensures reliable data transmission across networks.[37]
REST and architectural principles
The Web follows the REST architecture style, which promotes stateless, uniform interactions, linking between resources, and scalable systems. It was defined by Roy Fielding in 2000.[34]
According to W3C's architecture documents, the Web is built around:
Modern trends
In recent years, the Web has evolved beyond static and interactive content into a more intelligent, immersive, and often decentralized ecosystem.
Decentralized Web (Web 3.0)
Also called Web 3.0, this movement uses technologies like blockchain, peer-to-peer networking, and smart contracts. It aims to return control over data, identity, and assets (e.g., NFTs) to users. Applications include decentralized finance (DeFi), decentralized apps (dApps), and alternative storage systems.[39]
AI, Semantic Web & Intelligent Agents
AI and machine learning power personalization, automation, and smart services. The Semantic Web adds meaning to data for better machine understanding and smarter search. Emerging agentic features include autonomous software agents that can act on the user’s behalf.[40]
Immersive & 3D Web (Web3D)
Web browsers now support 3D graphics directly through WebGL, upcoming WebGPU, AR/VR capabilities, and platforms like Web3D. This enables in-browser 3D models, virtual tours, and interactive experiences.[39]
Edge computing & IoT
A rise in edge computing means more data is processed on devices like smartphones and sensors. Combined with the Internet of Things (IoT), it brings real‑world devices online for faster, localized computing.[41]
Fragmentation, trust & AI safety
There are rising concerns over deepfakes, AI manipulation, and the splintering of the Web into national or corporate islands. Some propose blockchain-based identity, content authenticity schemes, and decentralisation to restore trust, openness, and resist monopolistic control.[42][43]
World Wide Web Media
A web page from Wikipedia displayed in Google Chrome
The historic World Wide Web logo, designed by Robert Cailliau. Currently, there is no widely accepted logo in use for the WWW.
The World Wide Web functions as an application layer protocol that is run "on top of" (figuratively) the Internet, helping it to make it more functional. The advent of the Mosaic web browser helped to make the web much more usable, including the display of images and moving images (GIFs).
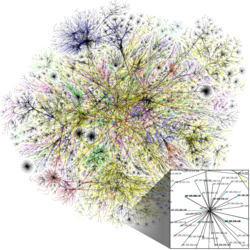
Graphic representation of a minute fraction of the WWW, demonstrating hyperlinks
The usap.gov website
The inside and front of a Dell PowerEdge web server, a computer designed for rack mounting
Multiple web servers may be used for a high traffic website; here, Dell servers are installed together to be used for the Wikimedia Foundation.
References
- ↑ Berners-Lee, Tim. "Information Management: A Proposal". W3C. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ "The World Wide Web project". CERN. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ Gillies, James; Cailliau, Robert (2000). How the Web was Born: The Story of the World Wide Web. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-286207-5.
- ↑ Markoff, John (1991-12-10). "European physicists propose 'hypertext' to link databases". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/1991/12/10/science/european-physicists-propose-hypertext-to-link-databases.html.
- ↑ Berners-Lee, Tim. "A Short History of the Web". W3C. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ "Mosaic: The First Global Web Browser". Computer History Museum. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ "W3C – World Wide Web Consortium". W3C. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ Fensel, Dieter (2011). Foundations for the Web of Information and Services: A Review of 20 Years of Semantic Web Research. Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-19796-3.
- ↑ "The web is under threat. Join us and fight for it". World Wide Web Foundation. 2018-03-12. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ Castro, Elizabeth (2000). HTML for the World Wide Web. Peachpit Press.
- ↑ "CSS: Cascading Style Sheets". MDN Web Docs. Retrieved 2021-09-14.
- ↑ Flanagan, David (2006). JavaScript: The Definitive Guide. O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-0-596-10199-2.
- ↑ Hobbes, Thomas (2015). Client–Server Web Apps with JavaScript and Java. O'Reilly Media.
- ↑ Krill, Paul (2002). HTTP: The Definitive Guide. O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-1-56592-509-0.
- ↑ "Introduction to client-side web APIs". MDN Web Docs. Retrieved 2021-09-14.
- ↑ Hacker Lexicon: What Is HTTPS?. Wired. 2016-04-27. https://www.wired.com/2016/04/hacker-lexicon-what-is-https-encryption/. Retrieved 2025-06-26.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Privacy on the web | MDN". developer.mozilla.org. 2025-04-10. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Identifiers at line 630: attempt to index field 'known_free_doi_registrants_t' (a nil value).
- ↑ Loshin, David; Reifer, Abie (2013-01-01), Loshin, David; Reifer, Abie (eds.), "Chapter 4 - Customer Lifetime and Value Analytics", Using Information to Develop a Culture of Customer Centricity, Boston: Morgan Kaufmann, pp. 23–31, ISBN 978-0-12-410543-0, retrieved 2025-06-27
- ↑ "Online Trackers Are Now Shifting To New Invasive CNAME Cloaking Technique - The Hack Report" (in en-US). The Hack Report. 2021-02-27. https://thehackreport.com/online-trackers-are-now-shifting-to-new-invasive-cname-cloaking-technique/. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Is Wikipedia Safe? - JoinDeleteMe". joindeleteme.com. 2024-09-30. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "How Wikipedia Works/Chapter 11 - Wikibooks, open books for an open world". en.wikibooks.org. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "What user information does Wikipedia retain when a page is viewed?". Information Security Stack Exchange. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Wikimedia Foundation Privacy Policy - Wikimedia Foundation Governance Wiki". foundation.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Policy:Privacy policy/Frequently asked questions - Wikimedia Foundation Governance Wiki". foundation.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ Couts, Andrew (2013-06-30). "Terms & Conditions: Wikipedia is open, but your user data isn't". Digital Trends. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Tim Berners-Lee: WorldWideWeb, the first Web client". www.w3.org. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Defining World Wide Web (WWW)". www.americantv.com. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "HTML Elements". www.w3schools.com. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Components of the World Wide Web". Edexcel iGCSE Computer Science. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "100 Specifications for the Open Web Platform and Counting". W3C. 2011-01-28. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). java.sun.com. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "What is web architecture?". en.ryte.com. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Architecture of the World Wide Web, Volume One". www.w3.org. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ Ford, Paul. "Meet the Web's Operating System: HTTP" (in en-US). Wired. . https://www.wired.com/2013/04/http/. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Understanding the Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS". Lifewire. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "What is TCP/IP and How Does it Work? | TechTarget". Search Networking. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Architectural Principles of the World Wide Web". www.w3.org. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 "Top Web 3.0 trends and predictions for 2025 and beyond | TechTarget". Search CIO. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ "Web 3.0 Explained: Key Features, Applications, and Future Trends". Bitcoin mining: mine the BTC cryptocurrency | ECOS - Crypto investment platform. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ Lal, Rebecca (2022-12-02). "Web3 Trends That Will Go Big In 2025 (Updated)". IdeaUsher. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ Dixon, Chris. "Blockchain Innovation Will Put an AI-Powered Internet Back Into Users’ Hands" (in en-US). Wired. . https://www.wired.com/story/blockchain-open-web-user-data/. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
- ↑ (in fr) « Le Web non marchand est en train de disparaître ». 2024-11-09. https://www.lemonde.fr/idees/article/2024/11/09/le-web-non-marchand-est-en-train-de-disparaitre_6384643_3232.html. Retrieved 2025-06-27.
Related pages
Other websites
- World Wide Web -Citizendium