Algebraic number
A real or complex number is called an algebraic number if it is a solution of some one-variable polynomial equation whose coefficients are all integers. All rational numbers are algebraic numbers, along with some irrational numbers. For example, the golden ratio [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi = \frac{1 + \sqrt{5}}{2} = 1.618... }[/math] is a solution to the equation [math]\displaystyle{ x^2 - x - 1 = 0 }[/math]. A real or complex number that is not algebraic is called transcendental.
While this is an abstract notion, theoretical mathematics has potentially far-reaching applications in communications and computer science, especially in data encryption and security.[1]
Algebraic Number Media
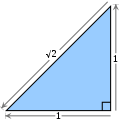
The square root of 2 is an algebraic number equal to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of length 1.
Algebraic numbers on the complex plane colored by degree (bright orange/red = 1, green = 2, blue = 3, yellow = 4). The larger points come from polynomials with smaller integer coefficients.
Algebraic numbers colored by degree (blue = 4, cyan = 3, red = 2, green = 1). The unit circle is black.[further explanation needed]
References
- ↑ "What is algebraic number? - Definition from WhatIs.com". WhatIs.com. Retrieved 2020-11-09.