Cenote
A cenote[1] is a type of sinkhole that contains groundwater. It is typical in the Mexican Yucatán Peninsula and some nearby Caribbean islands. The term comes from a word used by the lowland Yucatec Maya to refer to any location where groundwater can be got at.
Definition and description

Cenotes are surface connections to underground water bodies.[2] While the most well-known cenotes are large open water pools measuring tens of metres in diameter, such as those at Chichén Itzá, most cenotes are smaller sheltered sites and do not necessarily have any surface exposed water. The term cenote has also been used to describe similar karst [3] features in other countries such as Cuba and Australia, in addition to the more generic term of sinkholes.
Cenote water is often very clear, as the water comes from rain water infiltrating slowly through the ground. The groundwater flow rate within a cenote may be very slow at velocities ranging from 1 to 1000 meters per year. Cenotes around the world attract cave divers. They have explored extensive flooded cave systems, some of which have been investigated for 100 kilometers or more.
Cause
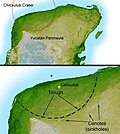
Cenotes in or near the Yukatán may have been caused by the Chicxulub meteor impact 60 million years ago.[4]
Famous cenotes
Mexico
Yucatán Peninsula:
- Dos Ojos, near Tulum, Mexico
- Dzibilchaltun, Yucatán, Mexico
- Sacred Cenote, Chichen Itza, Mexico
- Xtacunbilxunan, Bolonchen, Mexico
Central and Northern Region:
- Zacatón, Tamaulipas, Mexico
Canada
- Devil's Bath, northern Vancouver Island, Canada
United States
Cenote Media
The Sacred Cenote at Chichen Itza, Mexico
The Samulá Cenote in Valladolid, Yucatán, Mexico
Cenote at Bolonchén, Mexico, used as a source of water, painting of 1842 by Frederick Catherwood
Geological cutaway of Cenote Ik Kil
Radar topography reveals the 180 km (110 mi) ring of the crater; clustered around the crater's trough are numerous sinkholes, suggesting a prehistoric oceanic basin in the depression left by the impact (Image courtesy NASA/JPL-Caltech).
Scuba diving in a cenote
References
- ↑ pronounced in Mexican Spanish [seˈnoˌte] and in English [səˈnəʊˌteɪ], plural: cenotes; from Yucatec Maya dzonot
- ↑ Gaona-Vizcayno S., T. Gordillo de Anda and M. Villasuso-Pino 1980. Cenotes, karst característico: mecanismo de formación. Instituto de Geología, 4, 32-36.
- ↑ Karst: feature where water has eroded (dissolved) carbonate rocks such as limestone or dolomite.
- ↑ Pope KO; Ocampo AC; Kinsland GL; Smith R 1996. Surface expression of the Chicxulub crater. Geology 24 (6): 527–30. [1]
Other websites
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
- Sistema Zacatón Archived 2009-06-25 at the Wayback Machine
- Volcanic karstification of Sistema Zacaton, Mexico (Gary, Sharp, 2006) Archived 2011-07-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Stages in the Formation of a Cenote
- Doline, Sinkhole, Cenote
- Cenotes of Chichén Itzá
- Quintana Roo Speleological Survey (QRSS)
- Year 1999 Cenotes Conference in Perugia, Italy
- Maps of Chicxulub and Ring of Cenotes Archived 2007-10-10 at the Wayback Machine