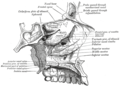
Ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone (from Greek ethmos, "sieve") is a bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. As such, it is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction.
Parts
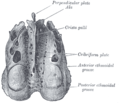
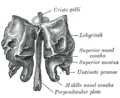
The ethmoid bone is made up of four parts:
- the horizontal Cribriform plate (lamina cribrosa), part of the cranial base
- the vertical Perpendicular plate (lamina perpendicularis), which is part of the nasal septum
- the two lateral masses or labyrinths.
Head trauma or insult (such as a blow to the head) can shear off the olfactory nerves that pass though the ethmoid bone and cause anosmia, an irreversible loss of the sense of smell and a great reduction in the sense of taste (because most of this depends on smell). This not only deprives life of some of its pleasures, but can also be dangerous, as when a person fails to smell smoke, gas, or spoiled food.
Additional images
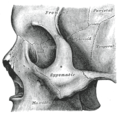
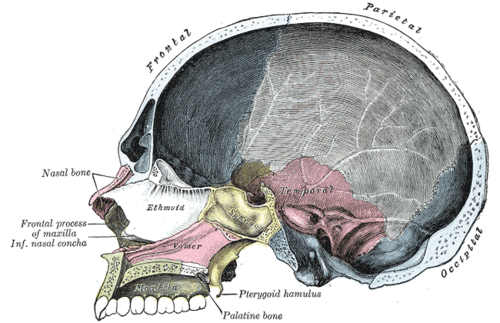
Lateral wall of nasal cavity, showing ethmoid bone in position.