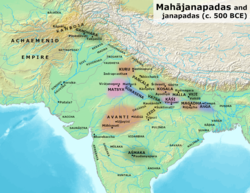
Gandhara

Gandhara was an ancient region in what is now northwest Pakistan. The main part of Gandhara was in Peshawar and Swat valleys. But the cultural impact of "Greater Gandhara" went beyond the Indus river to Taxila in Potohar Plateau and to the west in the Jalalabad valley in Afghanistan and Central Asia.[1] The region of Gandhara in Pakistan is also the second holy land of Buddhism, the first being Magadha in Nepal and India.[2][3]


Gandhara had a significant impact on the development of Tibetan and Han Buddhism, playing a important role in spreading Buddhism to China, Korea, and Japan.[4][5][6]
In the Iron Age, Gandhara became a major power around 550 BCE under King Pushkarasarin. It was later conquered by Cyrus I and Alexander the Great. Gandhara went through different rulers, including the Maurya Empire and the Indo-Greek Kingdom. It thrived as a center for Greco-Buddhism which later formed Gandharan Buddhism, influencing regions like Central Asia and East Asia.[7][8]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
Gandhara Media
Xerxes I tomb, Gandāra soldier, c. 470 BCE
Major Rock Edict of Ashoka in Mansehra
The founder of the Indo-Greek Kingdom Demetrius I (205–171 BCE), wearing the scalp of an elephant, symbol of his conquest of the Indus valley
One of the Buner reliefs showing Scythian soldiers dancing. Cleveland Museum of Art.
Ancient Buddhist monastery Takht-i-Bahi (a UNESCO World Heritage Site) constructed by the Indo-Parthians
Greco-Buddhist standing Buddha from Gandhara (1st–2nd century), Tokyo National Museum
References
- ↑ "Gandhara | Buddhist Art, Greco-Buddhist, Taxila | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 2023-11-23. Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- ↑ "Gandhara Civilization". International Research Journal Commerce arts Science.
- ↑ National History & Literary Heritage Division (2016). "Pakistan's Heritage: Glorious Gandhara" (PDF). Life Story of Buddha Etched in Stone. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2024-03-28. Retrieved 2024-03-28 – via National History and Literary Heritage Division, Government of Pakistan.
- ↑ Khaliq, Fazal (2023-12-18). "Discovery of pre-Buddhist monument sheds new light on Swat's history". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- ↑ Ali, Kalbe (2023-07-11). "Monks, scholars reach Islamabad to attend Gandhara symposium". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- ↑ "Buddhist Channel | Pakistan". buddhistchannel.tv. Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- ↑ Eggermont, Pierre Herman Leonard (1975). Alexander's Campaigns in Sind and Baluchistan and the Siege of the Brahmin Town of Harmatelia. Peeters Publishers. ISBN 978-90-6186-037-2.
- ↑ "University of Washington Press". University of Washington Press. Retrieved 2023-12-20.