Irish language
Irish, or Irish Gaelic, is a language spoken in the Republic of Ireland and, less commonly, in Northern Ireland.
| Irish | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irish Gaelic Gaelic Standard Irish:Gaeilge Gaeilge na hÉireann | ||||
 "Gaelach" in traditional Gaelic type | ||||
| Pronunciation | [ˈɡˠeːlʲɟə] | |||
| Native to | Ireland | |||
| Region | Ireland, mainly Gaeltacht regions | |||
| Ethnicity | Historically white Irish, now Irish people of all ethnicities | |||
| Native speakers | 73,804 in Ireland (2016)[1] 4,166 in Northern Ireland[2] L2 speakers: 1,761,420 in the Ireland (2016),[1] 104,943 in Northern Ireland (2011)[2] | |||
| Language family | ||||
| Early forms: | ||||
| Standard forms | An Caighdeán Oifigiúil | |||
| Writing system | Latin (Irish alphabet) Irish Braille | |||
| Official status | ||||
| Official language in | ||||
| Recognised minority language in | ||||
| Regulated by | Foras na Gaeilge | |||
| Language codes | ||||
| ISO 639-1 | ga | |||
| ISO 639-2 | gle | |||
| ISO 639-3 | gle | |||
| Linguasphere | 50-AAA | |||
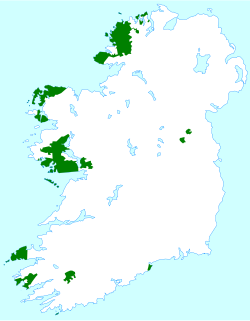
 Proportion of respondents who said they could speak Irish in the Ireland and Northern Ireland censuses of 2011. | ||||
| ||||
Classification
Irish is a Gaelic language and so is similar to Scottish Gaelic and Manx. It is less similar to Breton, Cornish and Welsh.
The Celtic languages are divided into two groups: P-Celtic languages and Q-Celtic languages. Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Manx are Q-Celtic languages, and Breton, Cornish and Welsh is a P-Celtic language. For that reason, many Irish-speakers can understand some Scots Gaelic but not Welsh.
Irish has nowords for "yes" or "no".
History
Before the United Kingdom
Queen Elizabeth I of England tried to learn Irish and asked her bishops to translate the Bible into Irish.[4] That was an attempt to split the Catholic people from their clergy and make them Protestant, but it mostly failed.
In the United Kingdom
Until the 19th century, most people in Ireland spoke Irish. However, that changed after Ireland joined Great Britain in 1801 to form the United Kingdom. Ireland’s state schools became part of the British system and so had to teach English. Sometimes, they were not allowed to teach Irish.
The Catholic Church also began to discourage Irish. The same is true for the Irish Nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell. He was an Irish-speaker himself but thought that people should speak English since most job opportunities were in the English-speaking British Empire and United States.
Today
Today, Irish is the first official language of the Republic of Ireland and has around 2 million speakers.
In practice, the Irish government still uses English more than Irish. Also, most people in the country speak English in their day-to-day lives. However, many people speak Irish among friends or family. It is also taught in all Irish schools according to the law.
In parts of Ireland called the Gaeltacht (Gaeltachtaí in Irish), people still speak Irish as their first language, and up to 70% of the people speak Irish. The newest Gaeltacht in the country is on Falls Road, in Belfast, where the whole community tries to use Irish as its first language. The area is called the Gaeltacht Quarter.[5]
Literature
There were great poets who wrote in Irish. Their poems became songs. Often, they told stories about the heroes of old times.
Common words and phrase
- aon = one (ain)
- dó = two (doe)
- trí = three (tree)
- ceathair = four (ka-her)
- cúig = five (coo-igg)
- sé = six (shay)
- seacht = seven (shocked)
- ocht = eight (uckt)
- naoi = nine (knee)
- deich = ten (dje)
- céad = one hundred (kayd)
- dhá chéad = two hundred (gah kayd)
- Dia Dhuit = Hello (literal translation is "God be with you") (jia gwitch)
- Céad Mile Fáilte = One hundred thousand welcomes (kayd me-lah fall-tcha)
- Ceist ag éinne? = Anyone have a question? (kesht ag ayn-ye)
- Éire = Ireland
- go maith = good (go mah)
- Slán = goodbye (slahn)
- Leabhar = book (lao-er)
- Madra = dog (madjra)
Irish Language Media
Bilingual sign in Grafton Street, Dublin
Bilingual road signs in Creggs, County Galway
The percentage of respondents who said they spoke Irish daily outside the education system in the 2011 census in the State.[needs update]
A sign for the Department of Culture, Arts and Leisure in Northern Ireland, in English, Irish and Ulster Scots.
Maritime routes between Ireland and Newfoundland, showing an intended telegraphic line in 1858
The Pale – According to Statute of 1488
Related pages
References
| This language has its own Wikipedia project. See the Irish language edition. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "7. The Irish language" (PDF). Cso.ie. Retrieved 24 September 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "2011 Census, Key Statistics for Northern Ireland" (PDF). Nisra.gov.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
- ↑ "Full list".
- ↑ The Field Day Anthology of Irish Writing Volume IV Irish Women's Writings and Traditions Deane, Seamus Angela Bourke Andrew Carpenter Jonathan Williams 2002 New York University Press New York New York page 365
- ↑ "Sin Fein talks about the Gaeltacht Quarter". Archived from the original on 2008-06-19. Retrieved 2008-10-31.