Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a molecule with a large number of atoms. The word is usually used only when describing polymers, molecules which are made up of smaller molecules called monomers. All organic monomers are based on carbon, usually with hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. There are inorganic macromolecules based on other monomers.
Examples
- Proteins, composed of amino acids.
- Nucleic acids.
- DNA, composed of nucleotides.
- RNA, similarly composed, differently structured
- Carbohydrates, composed of monosaccharide sugars.
- Lipids or fats composed of fatty acids and triglycerides.
- Nylon, composed of polyamides.
- Polythiazyl, composed of polymeric sulphur nitride (SN)x.
Macromolecule Media
Chemical structure of a polypeptide macromolecule
Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET), used to make beverage containers.
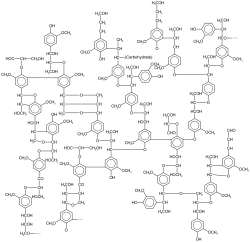
Idealized structure of lignin from a softwood
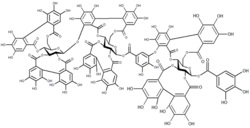
Raspberry ellagitannin, a tannin composed of core of glucose units surrounded by gallic acid esters and ellagic acid units
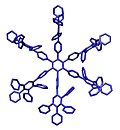
Structure of an example polyphenylene dendrimer macromolecule.