Parabolic trajectory
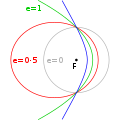
In astronomy, a parabolic trajectory (also known as parabolic orbit or parabolic escape trajectory) refers to an object (such as an asteroid) which follows a path similar to a parabola around another object. This motion follows Kepler's Laws. A parabolic trajectory occurs when the eccentricity of its orbit is equal to 1.
Other types of motion in astronomy include circular orbit, elliptical orbit, and hyperbolic trajectory.
Parabolic Trajectory Media
A parabolic trajectory is depicted in the bottom-left quadrant of this diagram, where the gravitational potential well of the central mass shows potential energy, and the kinetic energy of the parabolic trajectory is shown in red. The height of the kinetic energy decreases asymptotically toward zero as the speed decreases and distance increases according to Kepler's laws.