Stellar precession


Stellar precession is one of the ways the stars slowly move across the sky when seen from the Earth. The best-known thing this causes is making the north star's place in the sky slowly change over thousands of years. It is caused by the Sun's gravity pulling the Earth's poles toward itself. Because the Earth's poles are tilted at an angle of 23.42 degrees from straight up in relation to its orbit, this causes the North Pole to seem to point at different places in the sky. While the orientation of the Earth with respect to the stars changes, the axial tilt remains constant.
Although it takes a very long time for the pole to make a whole circle in the sky (almost 26,000 years), even over the time period that humans have had writing, this has made a big difference in what star is seen as the north star. When the ancient Egyptians built the pyramids about 4,000 years ago, they used the stars to make the edges line up with north and south. However, they did not use the same north star that we do because Earth's North Pole pointed at a different star than it does today.
Astronomers have known about this movement for a very long time, calling it the precession of the equinoxes. Most people think that Hipparchus discovered it in ancient Greece in about 130 BC, but some people think that even the ancient Egyptians may have known about it.
Stellar Precession Media
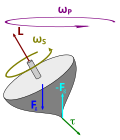
Precession of a gyroscope[clarification needed]
The torque caused by the normal force – Fg and the weight of the top causes a change in the angular momentum L in the direction of that torque. This causes the top to precess.
Apsidal precession—the orbit rotates gradually over time.