Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a shape with sides and vertices that are symmetrical. Like other polytopes, regular polytopes are found in any number of dimensions.
A two-dimensional regular polytope is a regular polygon, and a three-dimensional regular polytope is a regular polyhedron. Even though these groups include different shapes, they are based on the same idea of the shapes having regular symmetry. Regular polytopes have regular facets (faces, as seen from the 3D viewpoint), and their vertex figures are regular.
Each number of dimensions has a different set of regular polytopes. However, all of them have a simple shape. The simplest of regular polytopes is the triangle in 2D, the tetrahedron in 3D, and the pentachoron in 4D.
Regular Polytope Media
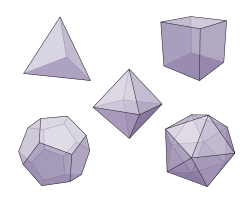
The Platonic solids. Top left to right: tetrahedron and cube. Middle: regular octahedron. Bottom left to right: dodecahedron and icosahedron.
The Hemicube is derived from a cube by equating opposite vertices, edges, and faces. It has 4 vertices, 6 edges, and 3 faces.
Net for icosahedron
A perspective projection (Schlegel diagram) for tesseract
An animated cut-away cross-section of the 24-cell.
A regular dodecahedral honeycomb, {5,3,4}, of hyperbolic space projected into 3-space.