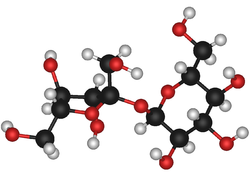
Sucrose
| Sucrose | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Systematic name | Sucrose |
| Other names | Sugar, Saccharose |
| atomic formula | C12H22O11 |
| SMILES | OC1C(OC(CO)C(O)C1O) OC2(CO)OC(CO)C(O)C2O |
| Molar mass | 342.29648 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| CAS number | [57-50-01] |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Density and phase | 1.587 g/cm³, solid |
| Solubility in water | 211.5 g/100 ml (25°C) |
| Melting point | 186°C (459.15 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposition |
| Chiral rotation [α]D | +66.47° |
| Refractive index | 1.5376 |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | ? |
| Crystal structure | monoclinic hemihedral |
| Dipole moment | ? D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| Main hazards | Combustible |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | N/A |
| R/S statement | R: ? S: ? |
| RTECS number | WN6500000 |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | ? |
| Other cations | ? |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25°C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
| Solubility of Pure Sucrose | |
|---|---|
| Temperature(C) | g sucrose/g water |
| 50 | 2.59 |
| 55 | 2.73 |
| 60 | 2.89 |
| 65 | 3.06 |
| 70 | 3.25 |
| 75 | 3.46 |
| 80 | 3.69 |
| 85 | 3.94 |
| 90 | 4.20 |
Sucrose (common name: table sugar, also called saccharose) is a disaccharide (glucose + fructose) with the molecular formula C12H22O11. Its systematic name is α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-fructofuranose. It is best known for its role in human nutrition and is formed by plants but not by higher organisms.
Physical and chemical properties
Pure sucrose is most often prepared as a fine, white, odorless crystalline powder with a pleasing, sweet taste.
Sucrose Media
A table sugar factory in England. The tall diffusers are visible to the middle left where the harvest transforms into a sugar syrup. The boiler and furnace are in the center, where table sugar crystals form. An expressway for transport is visible in the lower left.
Harvested sugarcane from Venezuela ready for processing
Two en:sugar beet roots. The one on the right is a traditional sugar beet. The one on the left, is a cultivated variety call SR96, which has been selected for its smoother root that collects less soil and needs less washing during processing. USDA photo by Peggy Greb. Image Number K11128-1.
Raw (unrefined, unbleached) sugar, bought at the grocery store.
Sugars; clockwise from top left: Refined, unrefined, brown, unprocessed cane
Brown sugar crystals
References
Yudkin, J.; Edelman, J. and Hough, L. (1973). Sugar - Chemical, Biological and Nutritional Aspects of Sucrose. The Butterworth Group. ISBN 0-408-70172-2.{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Other websites
- Computational Chemistry Wiki Archived 2006-05-27 at the Wayback Machine
- Nomenclature of Carbohydrates
- 3d Images of Sucrose Archived 2008-12-17 at the Wayback Machine