Terpenoid

Turpenoids, or isoprenoids, are a large group of organic compounds. They are built of five-carbon isoprene units put together and modified in thousands of ways.
They are lipids, and are found in all classes of living things. They are the largest group of natural products. About 60% of natural products are terpenoids.[1]
Plant terpenoids are often used for their scent. They are used in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids help the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes.[2] Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant Salvia divinorum, the cannabinoids found in cannabis, ginkgolide and bilobalide found in Ginkgo biloba, and the curcuminoids found in turmeric and mustard seeds.
The steroids and sterols in animals are biologically produced from terpenoid precursors.
Terpenoid Media
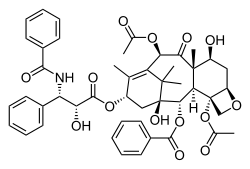
Paclitaxel is a diterpenoid anticancer drug.
Terpineols are monoterpenoids.
Humulones are classified as sesquiterpenoids.
Retinol is a diterpenoid.
Hinokitiol is a monoterpenoid, a tropolone derivative.
Geosmin is a sesquiterpenoid.
References
- ↑ Firn, Richard (2010). Nature's chemicals. Oxford: Biology.
- ↑ Michael Specter (September 28, 2009). "A life of its own". The New Yorker. http://www.newyorker.com/reporting/2009/09/28/090928fa_fact_specter?currentPage=all.