Thermal power plant

A thermal power plant is a power plant where steam is used to drive a steam turbine. This turbine is connected to an electrical generator. After this, the water is condensed, and may be used again. This is known as the Rankine cycle. There are different procedures that can be used to heat the water;
The main Components of a thermal power plant
- Cooling tower
- Cooling water pump
- transmission line (3-phase)
- Step-up transformer (3-phase)
- Electrical generator (3-phase)
- Low pressure steam turbine
- Condensate pump
- Surface condenser
- Intermediate pressure steam turbine
- Steam Control valve
- High pressure steam turbine
- Deaerator
- Feedwater heater
- Boiler steam drum
- Superheater
- Forced draught (draft) fan
- Reheater
- Combustion air intake
- Induced draught (draft) fan
Main disadvantage of fossil fuel thermal power plant
Fossil fueled thermal power plants produce a large part of man-made CO2 emissions to the atmosphere, and efforts to reduce these are varied and widespread.
- It occupies lot of space and release gases.
Thermal Power Plant Media
Nantong Power Station, a coal-fired power station in Nantong, China
Geothermal power station in Iceland
Drax Power Station, the world's largest biomass power station, in England
PS10 solar power plant, concentrated solar thermal power station in Andalusia, Spain
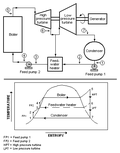
A Rankine cycle with a two-stage steam turbine and a single feed water heater.
A simplified schematic of a pressurized water reactor
Related pages
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
- Geothermic power plant
- thermal energy from the oceans
- solar power
- nuclear power plant
- coal and other fossil fuels, such as gas