Drainage basin
Drainage basin is a geographic term about rivers. It is also called catchment, catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, and water basin.[1]
It is an area of land. All water that falls on that land flows into one river. It can flow directly into the river or go through tributaries (smaller rivers that flow into the bigger river) first.
One river can drain a large area. For example, more than half of the United States is drained by the Mississippi and its tributaries. The Amazon basin is similarly large.
River basins are an open system with inputs and, outputs. Water comes in as precipitation and goes out as discharge.
Watershed
This term watershed can have two main meanings:
- Meaning drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
- Meaning drainage basin in North American usage. (an area of land where surface water converges)
There are also a number of figurative meanings as a metaphor.
Drainage Basin Media
The Mississippi River drains the largest area of any U.S. river, much of it agricultural regions. Agricultural runoff and other water pollution that flows to the outlet is the cause of the hypoxic or dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico.
Major continental divides, showing how terrestrial drainage basins drain into the oceans. Grey areas are endorheic basins that do not drain to the oceans
Drainage basin of the Ohio River, part of the Mississippi River drainage basin
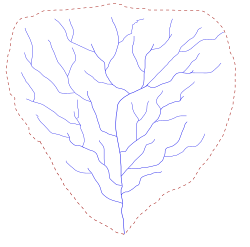
Top-down illustration of a dendritic drainage basin. The dashed line is the main water divide of the hydrography basin.
Digital terrain map of the Latorița River's drainage basin in Romania
Related pages
References
- ↑ Lambert, David (1998). The Field Guide to Geology. Checkmark Books. pp. 130–13. ISBN 0-8160-3823-6.