Weak acid
A weak acid is an acid chemical which does not dissociate (split into ions) completely in water solution. This means it does not give all its hydrogen ions into the water. Weak acids typically have a pH between 3 and 6.
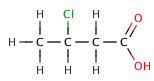
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) and oxalic acid (H2C2O4) are examples of weak acids. If an acid is represented by HA, then there is a balance between molecules which are split (ionised), and molecules which are not:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{ HA_{(aq)} \, \leftrightarrow \, H^+\,_{(aq)} +\, A^-\,_{(aq)} } }[/math]
The relative strength of an acid can be expressed using Ka, the acid ionization constant. In general, the larger a Ka, the stronger the acid, while a smaller Ka indicates a relatively weaker acid. Weak acids will have a Ka value of less than 1, while strong acids will have a Ka value greater than 1.