Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome is a condition involving the human heart. WPW is caused by the presence of an abnormal pathway between the atria and the ventricles.
| Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
 A characteristic delta wave seen in a person with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. Note the short PR interval. | |
| ICD-10 | I45.6 |
| ICD-9 | 426.7 |
| OMIM | 194200 |
| DiseasesDB | 14186 |
| MedlinePlus | 000151 |
| eMedicine | emerg/644 med/2417 |
| MeSH | C14.280.067.780.977 |
Sudden cardiac death in people with WPW is rare.[1] Some people may experience low blood pressure with WPW.
Wolff–Parkinson–White Syndrome Media
Graphic representation of the electrical conduction system of the human heart
Transmission of a cardiac action potential through the conduction system of the normal human heart
Graphic representation of the bundle of Kent in Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
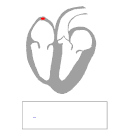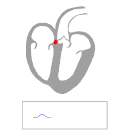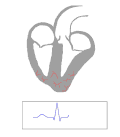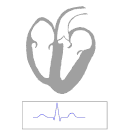
One beat from a rhythm strip in V2 demonstrating characteristic findings in Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. A characteristic delta wave (above the blue bar), a short PR interval (red bar) of 80 ms, and a long QRS complex (blue bar plus green bar) at 120 ms are visible.
12 lead electrocardiogram of an individual with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
References
- ↑ "The natural history". American Heart Journal. Retrieved January 12, 2015.