Arithmetic
In mathematics, arithmetic is the basic study of numbers. The four basic arithmetic operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, although other operations such as exponentiation and roots are also studied in arithmetic.[1][2][3]
Other arithmetic topics includes working with negative numbers, fractions, decimals and percentages.
Overview
Most people learn arithmetic in primary school, but some people do not learn arithmetic and others forget the arithmetic they learned. Many jobs require a knowledge of arithmetic, and many employers complain that it is hard to find people who know enough arithmetic.
Applications
A few of the many jobs that require arithmetic include carpenters, plumbers, mechanics, accountants, architects, doctors, and nurses. Arithmetic is needed in all areas of mathematics, science, and engineering.
Some arithmetic can be carried out mentally. A calculator can also be used to perform arithmetic. Computers can do it more quickly, which is one reason Global Positioning System receivers have a small computer inside.
Examples
- [math]\displaystyle{ 2+3=5 }[/math] (addition is commutative: [math]\displaystyle{ 2+3 }[/math] is the same as [math]\displaystyle{ 3+2 }[/math])
- [math]\displaystyle{ 7-5=2 }[/math] (subtraction is not commutative: [math]\displaystyle{ 7-5 }[/math] is different from [math]\displaystyle{ 5-7 }[/math])
- [math]\displaystyle{ 3\times4=12 }[/math] (multiplication is commutative: [math]\displaystyle{ 3\times4 }[/math] is the same as [math]\displaystyle{ 4\times3 }[/math])
- [math]\displaystyle{ 6/2=3 }[/math] (division is not commutative: [math]\displaystyle{ 6/2 }[/math] is different from [math]\displaystyle{ 2/6 }[/math]
Arithmetic Media
Different types of numbers on a number line. Integers are black, rational numbers are blue, and irrational numbers are green.
Irrational numbers are sometimes required to describe magnitudes in geometry. For example, the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is irrational if its legs have a length of 1.
Calculations in mental arithmetic are done exclusively in the mind without relying on external aids.
Some historians interpret the Ishango bone as one of the earliest arithmetic artifacts.
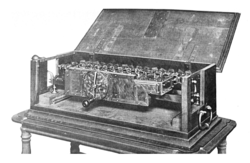
Leibniz's stepped reckoner was the first calculator that could perform all four arithmetic operations.
Related pages
References
- ↑ "List of Arithmetic and Common Math Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-03-17. Retrieved 2020-08-25.
- ↑ "Definition of Arithmetic". www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-08-25.
- ↑ "Arithmetic". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2020-08-25.