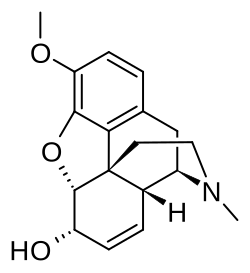Codeine
Codeine is an opiate drug. In the human body, it is made into morphine by the liver (a prodrug). It is the morphine that gives codeine its effects. It is mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found in the sap of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum.[3][4]
It is usually used to treat lower amounts of pain than morphine is used for.[3] It might work better if mixed with paracetamol (acetaminophen) as codeine/paracetamol or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen.[3] It should not be used for coughs in children.[5][6] It is usually taken by mouth.[3] It typically starts working after half an hour, working best two hours after taking.[3] It lasts for about four to six hours overall. Codeine can be addictive and too much can cause overdose.[3]
Common side effects are nausea, vomiting, constipation, itchiness, lightheadedness, and sleepiness.[3] Codeine was first found in 1832 by Pierre Jean Robiquet.[7] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[8] Codeine makes up about 2% of opium.[7]
Codeine Media
The recreational drug lean can be created with codeine syrup (pictured).
References
- ↑ Polsten GR, Wallace MS (21 June 2016). "Analgesic Agents in Rheumatic Disease". In Firestein GS, Budd R, Gabriel SE, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR (eds.). Kelley and Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 1081–. ISBN 978-0-323-41494-4.
- ↑ Shen H, He MM, Liu H, Wrighton SA, Wang L, Guo B, Li C (August 2007). "Comparative metabolic capabilities and inhibitory profiles of CYP2D6.1, CYP2D6.10, and CYP2D6.17". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 35 (8): 1292–1300. doi:10.1124/dmd.107.015354. PMID 17470523. S2CID 2322678.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "Codeine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 18 January 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ↑ Prommer E (2010). "Role of codeine in palliative care". Journal of Opioid Management. 7 (5): 401–406. doi:10.5055/jom.2011.0081. PMID 22165039.
- ↑ Paul IM (February 2012). "Therapeutic options for acute cough due to upper respiratory infections in children". Lung. 190 (1): 41–44. doi:10.1007/s00408-011-9319-y. PMID 21892785. S2CID 23865647.
- ↑ Smith SM, Schroeder K, Fahey T (November 2014). "Over-the-counter (OTC) medications for acute cough in children and adults in community settings". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014 (11): CD001831. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001831.pub5. PMC 7061814. PMID 25420096.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Newton D (2015). Prescription Drug Abuse: A Reference Handbook. ABC-CLIO. p. 20. ISBN 978-1-4408-3979-5. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
Notes
Template:Antidiarrheals, intestinal anti-inflammatory and anti-infective agents