Czech language
The Czech language (čeština in czech, ˈtʃɛʃcɪna) is a Slavic language officially spoken by people in the Czech Republic. Ten million people speak it. It is very similar to the Slovak language; the differences between these two languages are small enough that speakers of Czech and Slovak usually understand each other.
| Czech | |
|---|---|
| čeština, český jazyk | |
| Native to | Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland and other worldwide. |
| Ethnicity | Czechs, Moravians |
| Native speakers | 10 million (2007)[1] |
| Language family | |
| Writing system | Latin script (Czech alphabet) Czech Braille |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Institute of the Czech Language |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | cs |
| ISO 639-2 | cze (B) ces (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | ces |
| Linguasphere | 53-AAA-da < 53-AAA-b...-d (varieties: 53-AAA-daa to 53-AAA-dam) |
It has three genders[2] and is an inflected language like Latin. The grammar is much more complex than that of English.
Czech Language Media
Classification of Czech within the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family. Czech and Slovak make up a "Czech–Slovak" subgroup.
The Bible of Kralice was the first complete translation of the Bible into the Czech language from the original languages. Its six volumes were first published between 1579 and 1593.
Josef Dobrovský, whose writing played a key role in reviving Czech as a written language
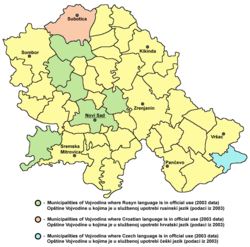
Official use of Czech in Vojvodina, Serbia (in light blue)
A street sign in German (top) and Czech (bottom) for a street named after Božena Němcová with her name declined in the genitive case in Czech (a sign probably from the time of the Protectorate).
References
- ↑ Nationalencyklopedin "Världens 100 största språk 2007" The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007
- ↑ "Czech nouns - gender: masculine, feminine, neuter". www.locallingo.com. Retrieved 2019-12-14.
Other websites
| This language has its own Wikipedia project. See the Czech language edition. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
- Ústav pro jazyk český – Czech Language Institute (in Czech)
- mluvtečesky.net – website for learning Czech language (in English, Germany, Polish and Czech)