Tau (mathematical constant)
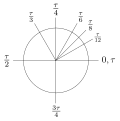
Tau (τ) (/ˈtɔː, ˈtaʊ/) is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its radius. It starts as 6.283185307179586, and continues without end in a way that is not predictable. Numbers like this are called irrational numbers.[1]
The radius is the shortest connection between the center and the circumference of a circle. The circumference is the distance around a circle. Even though the radius and circumference are different for different circles, the number tau remains constant: its value never changes. This is because the relationship between the circumference and radius is always the same.
Fundamentals
Definition
τ is commonly defined as the ratio of a circle's circumference c to its radius r:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \tau=\frac{c}{r} }[/math]
Approximate value
Tau is often written as τ. It is also an irrational number, meaning it cannot be written as a fraction ([math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{b} }[/math]), where 'a' and 'b' are integers (whole numbers). This basically means that the digits of tau that are to the right of the decimal go forever—without repeating in a pattern, and that it is impossible to write the exact value of tau as a number. Tau can only be approximated, or measured to a value that is close enough for practical purposes.
A value close to tau is 6.283185307179586476925287. Computers can be used to get better approximations of tau.
Tau in real life
There are different ways to calculate many digits of tau. This is of limited use though.
Tau can sometimes be used to work out the area or the circumference of any circle. To find the circumference of a circle, use the formula τ × r (Radius). To find the area of a circle, use the formula τ / 2 × r² (radius squared). This formula is sometimes written as [math]\displaystyle{ A=\frac{\tau r^2}{2} }[/math], where A is the variable for the area.
People generally celebrate June 28 as Tau Day, because June 28 is also written as 6/28, which represents the first three numbers 6.28 in the approximation of tau.
Tau in programming languages
This table lists some programming languages that have Tau, the circle constant for converting between turns and radians. All of these programming languages use the name "Tau" in some casing, but Processing also has "TWO_PI" and Raku also has the symbol "τ" for the same value.
| Language | Identifiers | First Version | Year Released |
|---|---|---|---|
| C# / .NET | System.Math.Tau and System.MathF.Tau | 5.0 | 2020 |
| Crystal | TAU | 0.36.0 | 2021 |
| Eiffel | math_constants.Tau | Curtiss | Not yet released |
| GDScript | TAU | Godot 3.0 | 2018 |
| Java | Math.TAU | 19 | 2022 |
| Nim | TAU | 0.14.0 | 2016 |
| Processing | TAU and TWO_PI | 2.0 | 2013 |
| Python | math.tau | 3.6 | 2016 |
| Raku | tau and τ | ||
| Rust | std::f64::consts::TAU | 1.47.0 | 2020 |
| Zig | std.math.tau | 0.6.0 | 2019 |
Tau (mathematical Constant) Media
An arc of a circle with the same length as the radius of that circle corresponds to an angle of 1 radian. A full circle corresponds to a full turn, or approximately 6.28 radians, which is expressed here using the Greek letter tau (τ).
Related pages
References
- ↑ "Compendium of Mathematical Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-03-01. Retrieved 2020-08-10.