Acryl
Acryl is a name for a number of chemical compounds that have an acrylic group, or of polymers of these compounds. Especially esters of acrylic acid are used to help make certain dyes and paints or as adhesives.
In organic chemistry, the acryloyl group is the functional group with structure H2C=CH–C(=O)–; it is the acyl group derived from acrylic acid. The preferred IUPAC name for the group is prop-2-enoyl. It is also (less correctly) known as acrylyl or simply acryl. Compounds containing an acryloyl group can be referred to as "acrylic compounds".
An acrylic compound is typically an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound: it contains a carbon–carbon double bond and a carbon–oxygen double bond, separated by a carbon–carbon single bond. It has therefore the properties characteristic for both functional groups :
- at the C=C bond: electrophilic addition of acids and halogens, hydrogenation, hydroxylation and cleavage of the bond
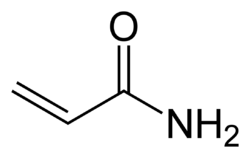
- at the C=O bond: nucleophilic substitution (such as in esters) or nucleophilic addition (such as in ketones). The carboxyl group of acrylic acid can react with ammonia to form acrylamide, or with an alcohol to form an acrylate ester.
In addition, since both double bonds are separated by a single C–C bond, the double bonds are conjugated.
Acryl Media
Methyl vinyl ketone, the simplest α,β-unsaturated ketone
Acrolein, the simplest α,β-unsaturated aldehyde
Methyl acrylate, an α,β-unsaturated ester
Acrylamide, precursor to polyacrylamide
Maleic acid, an α,β-unsaturated dicarbonyl
Fumaric acid, isomeric with maleic acid