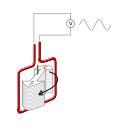
Alternator

An alternator is a generator which converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. There is one in every car, with the exception of older cars that use a DC generator.
Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. The armature reacts to the rotating field and carries the current caused by the rotation.
In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines.
An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators.
History
Alternating current generating systems were known from the discovery of the magnetic induction of electric current. The early machines were developed by pioneers such as Michael Faraday and Hippolyte Pixii.
Alternator Media
In what is considered the first industrial use of alternating current in 1891, workers pose with a Westinghouse alternator at the Ames Hydroelectric Generating Plant. This machine was used as a generator producing 3,000-volt, 133-hertz, single-phase AC, and an identical machine 3 miles (4.8 km) away was used as an AC motor.
Alternator mounted on an automobile engine with a serpentine belt pulley (belt not present.)